Unmasking Digital Fakes with AI Reverse Image Search
When we talk about an AI reverse image search, we're not just looking for an exact copy of a picture. We're using artificial intelligence to hunt down images that are conceptually similar. It’s a huge leap from traditional tools that just match pixels. AI gets the bigger picture—understanding the content, style, and even the context of an image. This lets it uncover everything from heavily edited photos to similar scenes and even AI-generated fakes.
The Evolution from Pixel Matching to Content Understanding

Think of standard reverse image search tools like Google Images or TinEye as digital bloodhounds sniffing out an exact scent. They work by creating a unique digital fingerprint for an image and then scouring the web for perfect matches. This is fantastic for pinpointing the original source of a photo or seeing where it's been reposted without any changes.
But their trail goes cold the moment an image is altered. A simple crop, a new filter, or even adding a bit of text is often enough to throw these traditional systems off. The direct pixel-to-pixel connection is broken, and the search hits a dead end.
This is exactly where AI reverse image search picks up the trail. It goes beyond just matching pixels and dives into true content comprehension. Instead of seeing a random assortment of colors and shapes, an AI model deciphers what the image is actually about.
An AI doesn't just see a "picture of a dog." It recognizes a golden retriever, playing in a park, with a red ball, during sunset. This deep contextual analysis is its superpower.
This ability to understand the story within the frame allows AI tools to do things that were simply out of reach for older search engines. They can connect the dots between images that look quite different but share a common theme, giving you a much more meaningful and useful set of results.
To put it simply, here’s a quick breakdown of how these two approaches stack up.
Traditional vs AI Reverse Image Search at a Glance
This table highlights the fundamental differences in what standard and AI-enhanced reverse image search technologies can actually do.
| Feature | Traditional Reverse Image Search | AI Reverse Image Search |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Finds exact or near-exact duplicates of an image. | Finds conceptually related and visually similar images. |
| Core Technology | Pixel matching, digital fingerprinting (hashing). | Neural networks, feature embeddings, content analysis. |
| Handles Modifications | Poorly. Cropping, filters, or text can easily break the match. | Excellently. Can identify images despite significant alterations. |
| Understands Content | No. It only sees patterns of pixels, not the subject matter. | Yes. It interprets objects, scenes, styles, and context. |
| Generative AI Detection | Not possible. It has no mechanism to identify synthetic content. | Yes. Specialized models can detect artifacts of AI generation. |
| Typical Use Case | Finding the original source of an image; flagging plagiarism. | Verifying manipulated media, discovering related concepts. |
As you can see, the shift to AI isn't just an upgrade—it's a complete change in capability, opening the door to more sophisticated and necessary forms of digital investigation.
Key Capabilities of AI Search
Moving from basic matching to AI-powered analysis unlocks some powerful new abilities. These tools are no longer just for finding duplicates; they're for verification, discovery, and protecting the integrity of information.
- Conceptual Similarity: Find images that share a theme, even if they look nothing alike. A search using a photo of a sleek, minimalist living room might bring back examples of Scandinavian interior design or Bauhaus architecture.
- Modified Version Detection: AI can easily spot an image even after it's been heavily cropped, resized, or had its colors changed. This is critical for tracking how misinformation or propaganda spreads.
- Generative-AI Detection: Some of the most advanced models can identify the tell-tale signs left behind by image generators like Midjourney or DALL-E. They spot the subtle artifacts and unnatural patterns that separate a real photo from a synthetic one.
These advancements are turning reverse image search from a simple file-lookup system into an essential analytical tool. For anyone who needs to confirm the authenticity and origin of an image, it’s a non-negotiable part of the modern toolkit.
How AI Image Verification Technology Works
To really get what’s happening inside an AI reverse image search tool, you have to look past simple pixel-matching. Modern verification technology is more like a digital forensics lab, digging deep into an image’s structure. It uses a combination of powerful techniques to not only find similar pictures but also to figure out if an image is authentic or a sophisticated fake.
This isn't just about comparing two images side-by-side. Instead, AI models transform pictures into complex sets of numbers, which allows for a much more flexible and profound analysis of their content and origin. This is the secret sauce: shifting from just looking at pictures to analyzing their data.
Feature Embeddings: The Image's DNA
Think of a photo not as one solid thing, but as a collection of thousands of tiny features—the lines, shapes, textures, colors, and objects inside it. An AI's first job is to spot these core components and distill them into a compact numerical signature. We call this a feature embedding.
This embedding is basically the image's unique DNA. It's a dense string of numbers that mathematically describes everything the AI "saw" in the picture.
- Contextual Understanding: This digital DNA goes beyond just listing pixels; it captures how objects relate to each other. It knows a "wheel" is part of a "car" and a "tree" belongs in a "forest."
- Resilience to Change: Because it’s built on core concepts, this embedding stays remarkably consistent even if you crop the image, resize it, or slap a filter on it. The fundamental "DNA" doesn't really change.
This is exactly why an AI can spot a photo of the Eiffel Tower whether it's a sunny day shot or a moody, black-and-white art photo. The essential features defining the landmark are locked into that embedding, making the match happen.
Perceptual Hashing: A Fuzzy Fingerprint
While feature embeddings are all about understanding an image's content, perceptual hashing is about creating a "fuzzy fingerprint" of its overall look and feel. This is very different from a cryptographic hash, which changes dramatically if you alter even a single pixel. A perceptual hash is designed to stay similar for images that look similar to the human eye.
It's a bit like summarizing a 500-page book in a single paragraph. You’d capture the main plot and themes, but a few typos or rephrased sentences in the original wouldn't change your summary. That’s what perceptual hashing does for images—it creates a compact hash that shrugs off minor, insignificant differences.
This technique is the key to finding near-duplicates. It allows systems to flag an image that has been slightly edited or compressed—a common trick used to spread altered media without getting caught by traditional search engines.
This technology is a crucial first line of defense. The fake image detection market is projected to balloon from $2.08 billion to $4.21 billion by 2029, a surge driven by the urgent need to fight the flood of manipulated visuals. With deepfake videos jumping by 550% in recent years, perceptual hashing helps us track how these nearly identical fakes spread online.
Generative Artifact Detection: Digital Forensics
The most sophisticated layer in an AI reverse image search is generative artifact detection. This is where the AI stops acting like a librarian and becomes a digital forensic investigator, hunting for the specific clues that an image was cooked up by an AI model. For anyone curious about how these systems are built from the ground up, a great guide on AI engineering services provides a look under the hood.
As good as AI image generators are, they aren't perfect. They often leave behind subtle, almost invisible traces of their synthetic origins. A specialized detector is trained on millions of real and AI-generated images, learning to spot these tell-tale signs. You can dive deeper into the specifics of this process in our guide to AI image identification.
Here are a few common artifacts the AI looks for:
- Unnatural Textures: Surfaces like skin, wood, or fabric might look a little too smooth or have repeating patterns you’d never find in nature.
- Inconsistent Lighting: You might see shadows falling in the wrong direction or light bouncing off surfaces in a way that just defies physics.
- Pixel-Level Noise: The AI can analyze an image’s frequency patterns and often finds a distinct "digital noise" signature that is characteristic of certain generative models.
- Logical Flaws: Sometimes the AI catches strange details a human might miss, like a person with six fingers or reflections that don't match the surrounding environment.
By weaving these three layers together—understanding the content, identifying near-duplicates, and hunting for synthetic fingerprints—AI verification tools offer a powerful, multi-pronged defense against digital deception.
A Practical Workflow for Verifying Images
Knowing the theory is one thing, but putting it into practice is where it counts. For journalists, moderators, and fact-checkers on the front lines, a reliable, step-by-step process is the only way to make quick, accurate judgments. A scattershot approach just won’t work when deadlines are tight and the stakes are high.
The best strategy isn't about finding one magic tool; it's about layering different verification methods. This approach creates a powerful, multi-stage defense that can catch everything from simple reposts to sophisticated, AI-generated fakes. Each step builds on the last, giving you an increasingly clear picture of an image’s authenticity.
Step 1: Start with a Traditional Baseline
Before you jump into advanced AI tools, your first move should always be a baseline check using traditional reverse image search engines. Tools like Google Images and TinEye are still the champions of tracing an image’s digital footprint across the web. Their main job is to find exact or near-exact matches, and they do it well.
This first step is all about answering a few basic questions fast:
- When did this image first appear online? A TinEye search can often pinpoint the earliest indexed date of an image, which is gold for figuring out its origin.
- Where has it been used before? If the photo has popped up on unrelated news sites, stock photo platforms, or old blogs, you can often debunk a false narrative in minutes.
- Is it original or repurposed? If a photo supposedly from a recent event shows up in articles from five years ago, your work is done.
Think of this baseline search as your first filter. It weeds out the low-hanging fruit—old images passed off as new—and gives you the historical context you need to start your investigation. It’s like checking the alibi of your visual evidence.
Step 2: Uncover Alterations with AI Search
After establishing the image's history, it’s time to hunt for modified versions and conceptually similar fakes that a standard search would miss. This is where a true AI reverse image search comes in. These tools don't just match pixels; they understand the content of an image, allowing them to connect the dots between visually different but related images.
For instance, a traditional search might fail if someone has heavily cropped a photo, slapped on a dramatic color filter, and added misleading text. An AI-powered search, on the other hand, can often see right through those changes by recognizing the core objects and composition. It’s essentially identifying the image's "DNA," even if its appearance has been tweaked. This is crucial for tracking how a single piece of visual misinformation morphs as it spreads.
This three-part process illustrates the flow, starting with basic origin tracing (DNA), moving to identifying similar versions (Fingerprint), and finishing with a deep forensic analysis (Artifacts).
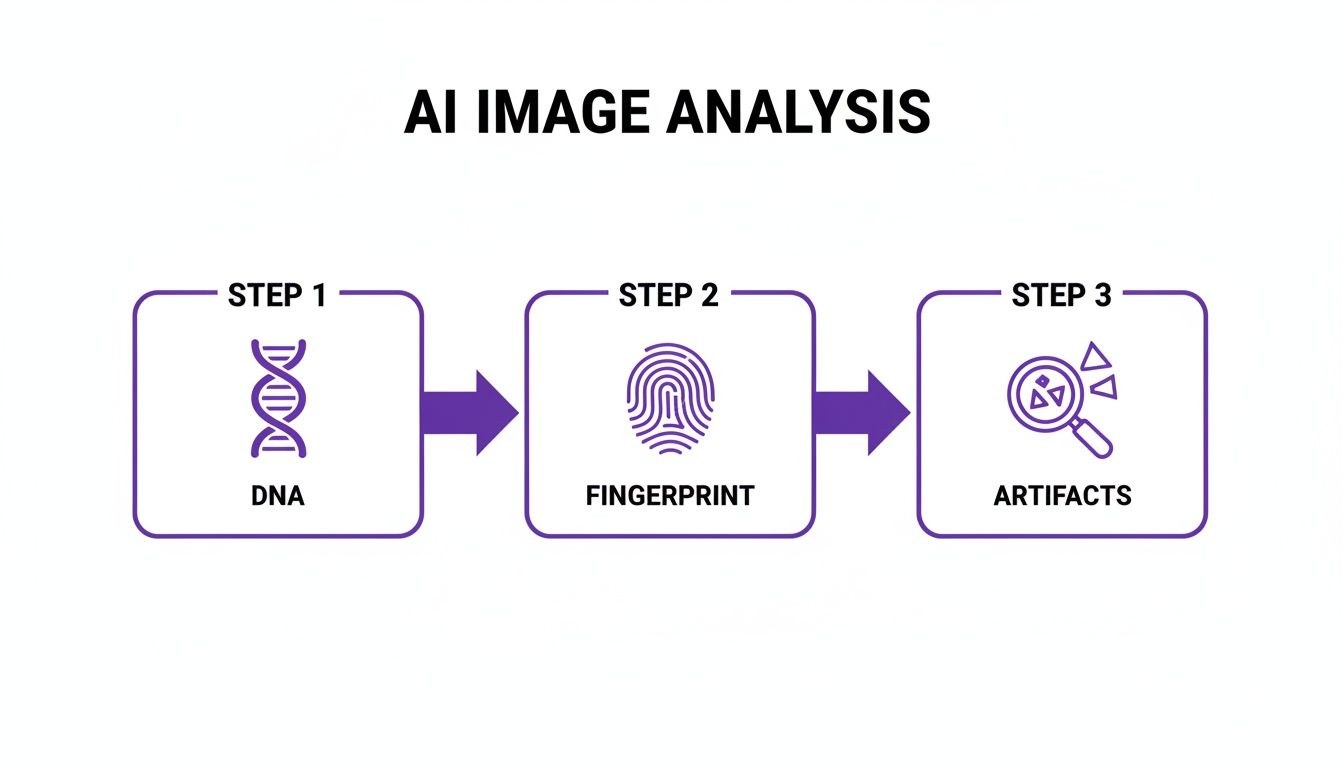
This layered workflow ensures you're covering all your bases, leaving very little room for manipulated or synthetic media to slip through the cracks.
Step 3: Perform a Forensic Scan for Artifacts
The final, and often most decisive, step is to figure out if the image itself is a synthetic creation. This calls for a specialized tool like an AI image detector. Think of it as a forensic scanner that looks for the subtle, digital fingerprints left behind by generative AI models.
These detectors are trained on millions of real and AI-generated images, which teaches them to spot the tell-tale signs of artificial creation that are often invisible to us. They analyze the image for things like:
- Unnatural lighting and inconsistent shadows.
- Strange, repeating patterns in textures like skin, hair, or fabric.
- Pixel-level noise that is characteristic of specific generative models.
- Logical impossibilities, like mangled hands or bizarre architectural details.
A dedicated AI detector gives you a clear confidence score on an image's authenticity. This moves your investigation beyond finding where an image has been and helps you answer the most important question: what is this image?
For a deeper dive into how these tools break down visual information, this analysis of photos offers a great look at the technical clues they search for.
By combining a traditional search, an AI-powered similarity search, and a forensic AI detection scan, you create a solid workflow that gives you a comprehensive and defensible verdict on any image’s origin and authenticity.
Putting It All to Work: AI Image Detection in the Real World
It's one thing to talk about the theory, but where does this technology actually make a difference? An AI reverse image search isn't just some abstract idea; it's a powerful tool being used right now to solve real, complex problems. From newsrooms fighting the tide of fake news to online stores battling fraud, these examples show just how valuable advanced image verification has become.

These scenarios go far beyond just finding a simple copy of a photo. They demonstrate how AI’s ability to analyze an image's content, context, and hidden artifacts delivers critical intelligence when it matters most.
Debunking Misinformation in Journalism
In the heat of a breaking news story, a single, compelling image can steer the public narrative before anyone has a chance to check the facts. Journalists are on the front lines, constantly facing viral photos that demand immediate and accurate verification.
The Problem: A dramatic photo supposedly showing sharks swimming down a flooded highway after a hurricane starts spreading like wildfire on social media. It fuels panic and wildly distorts the reality of the situation.
The AI Solution: A fact-checking team ran a traditional reverse image search, but it came up empty. The image wasn't a copy; it was a clever composite. So, they turned to an AI-powered tool. Instead of looking for an exact match, this system used feature embeddings to break the image down into its core components: the flooded street, the cars, and the sharks.
The Outcome: The AI search hit the jackpot. It traced the separate elements back to their original sources. The flooded street was from a different hurricane years ago, and the sharks were pulled from a well-known nature documentary. With this concrete proof, the news outlet could issue a swift and decisive debunking, showing their audience exactly how the fake was made and stopping the misinformation cold.
Protecting E-Commerce Marketplaces
Trust is the currency of any online marketplace, but it's incredibly fragile. A common scam involves using stolen or completely fake product photos to trick people into buying something that's low-quality or doesn't even exist.
By identifying fraudulent listings before they can harm consumers, e-commerce platforms protect both their revenue and their reputation. This proactive defense is only possible with automated, AI-driven verification.
The Problem: A major online retailer noticed a surge in complaints from customers saying the products they received looked nothing like the photos online. Scammers were creating new accounts and listing popular gadgets using slick, professional images scraped from other sites or even generating hyper-realistic fakes with AI.
The AI Solution: The platform plugged in an API to run a real-time AI reverse image search on every single new product photo.
- Perceptual Hashing: The system first looked for near-duplicates of existing product shots and known stock photos, instantly flagging stolen content.
- Generative Artifact Detection: For images that seemed original, a second AI model scanned for the subtle giveaways of AI generation, like unnaturally perfect reflections or weirdly smooth textures.
The Outcome: The system immediately flagged hundreds of fraudulent listings. The platform's trust and safety team was able to suspend the accounts before a single sale was made. Considering that scams involving stolen images cost consumers $48 billion, this kind of robust, automated verification is a massive financial shield. You can explore more on the growing image recognition market over at Fortune Business Insights.
Safeguarding Creative Copyright for Artists
For photographers and digital artists, their work is their brand and their income. When their images are used without permission, it not only devalues their craft but directly hurts their bottom line.
The Problem: A digital artist was horrified to find her unique character designs showing up on t-shirts and mugs sold across dozens of online stores. The content thieves were making small tweaks—flipping the image or changing background colors—to sneak past basic image-matching software.
The AI Solution: The artist turned to an AI search tool designed to understand artistic style. This AI didn't just match pixels; it was trained to recognize her specific brush strokes, color palette, and character proportions. By uploading her portfolio, she essentially gave the AI a stylistic "fingerprint" to search for.
The Outcome: The tool scoured the web and found every single unauthorized use, even the altered versions. Armed with a mountain of evidence, the artist could fire off takedown notices and finally regain control over her intellectual property.
Comparing the Best AI Reverse Image Search Tools
Picking the right tool for an AI reverse image search really boils down to one simple question: what are you trying to accomplish? Not all of these platforms are built the same. Some are fantastic for general discovery, while others are designed for the kind of deep, forensic verification needed to expose fakes. Knowing the difference is the key to getting results that are not just fast, but genuinely useful.
The demand for these tools is exploding, and for good reason. The reverse image search market is currently valued at around $2 billion and is expected to jump to $6 billion by 2033. That incredible growth is being fueled by journalists, researchers, and fact-checkers on the front lines, all needing better ways to track where images come from and stop misinformation in its tracks. You can find a deeper dive into these market trends at DataInsightsMarket.com.
General-Purpose Visual Search Engines
For everyday searches—like identifying a plant in your garden or finding a product you saw online—the big, general-purpose tools are your best bet. They’re built right into the search engines we already use, designed to cast the widest net possible across the web.
- Google Lens: This is the undisputed champ for broad searches. Built into Google Search and Android phones, its real strength is identifying just about anything: objects, landmarks, text in a photo, and products. It’s perfect for answering the question, "What is this, and where can I find more like it?"
- Bing Visual Search: Microsoft’s answer to Lens is a very capable competitor. It does much of the same, letting you search with an image to find similar items or see where else that picture appears online. It’s a great alternative and sometimes surfaces results that Google misses.
Think of these as your first stop for quick, surface-level questions. They're not specialized for tracking an image's original source or spotting sophisticated digital edits.
Specialized Image Origin Trackers
When your mission is to play detective and trace an image’s journey across the internet, you need a specialist. These platforms are laser-focused on finding exact copies and near-duplicates to build a clear timeline of where and when an image has appeared.
TinEye: This is the gold standard for digital archivists and journalists. TinEye's entire purpose is to find out where an image originated, how it’s being used today, and if altered versions are floating around. With a massive database of tens of billions of images, it is exceptionally good at finding the earliest indexed version of a photo.
Unlike Google or Bing, TinEye isn't trying to find things that look like your image. It’s built to deliver a clean, chronological history of your specific image.
Dedicated AI Image Detectors
This last category of tools is built to answer one of the most critical questions of our time: was this image made by a person or an AI? Much like how specialized social media search engines dig up textual information, these AI detectors are powerful forensic tools for visuals.
- AI Image Detector: This tool has one job: forensic analysis. It scans for the subtle, tell-tale signs of AI generation—the unnatural textures, odd pixel patterns, and other invisible artifacts that give fakes away. Instead of just matching images, it delivers a clear confidence score on whether the image is authentic. To get a better sense of the technology behind it, take a look at our guide on what makes an image ai detector tick.
For anyone working in a high-stakes field like a newsroom or a content moderation team, this kind of tool isn't just helpful—it's essential.
Feature Comparison of Leading Reverse Image Search Tools
So, how do you choose? The best approach is often layered. You might start broad with Google Lens, dig into the history with TinEye, and then run a final authenticity check with AI Image Detector. To make it easier, here’s a quick breakdown of which tool to use and when.
| Tool | Primary Use Case | AI Detection Focus | Privacy Policy | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Google Lens | Object recognition & finding similar public images. | Minimal; not its primary function. | Tied to Google's standard user data policies. | General discovery and shopping. |
| Bing Visual Search | Finding visually similar images and web pages. | None; focused on visual search. | Governed by Microsoft's privacy statement. | Competitive analysis & broad search. |
| TinEye | Tracking the origin and modification history of an image. | None; focuses on matching and history. | Strong privacy; uploaded images are not indexed. | Journalists and copyright holders. |
| AI Image Detector | Determining if an image is human-made or AI-generated. | High; specialized in generative artifact detection. | Strict; images are not saved or shared. | Fact-checkers and platform moderators. |
Ultimately, having the right tool for the job saves time and, more importantly, helps ensure the visual information you're working with is trustworthy.
Your Questions About AI Image Search, Answered
As AI tools pop up everywhere, it's totally normal to have questions about how they work, where they fall short, and what happens to your data. An AI reverse image search is an incredibly powerful tool, but you need to understand its quirks to use it well.
Let's dive into some of the most common questions people have. We'll cover everything from how people try to trick these systems to the serious privacy issues that come with uploading your photos online. Getting clear answers helps you make smarter, safer choices.
Can AI Image Detectors Be Fooled?
The short answer is yes, but it’s getting much harder. The relationship between AI image generators and the tools built to detect them is a constant cat-and-mouse game. As the generators get better at creating realistic images, the detectors have to evolve right alongside them.
In the early days, AI-generated images were a breeze to spot. You’d see obvious flaws like mangled hands, distorted faces, or weird, dream-like backgrounds. Now, the tell-tale signs are far more subtle. Still, a determined person can sometimes fool a detector with a few tricks:
- Adding Digital Noise: Sprinkling a layer of random "grain" or static over an image can sometimes confuse the patterns an AI detector is looking for.
- Compression and Resizing: Heavily compressing a JPEG or repeatedly saving and resizing an image can degrade the digital artifacts left by AI, making them much harder to spot.
- Manual Editing: A skilled digital artist can use Photoshop to manually paint over or correct the tiny imperfections left behind by an AI generator.
- "Hybrid" Images: This is a clever one. Combining real photographic elements with AI-generated backgrounds (or vice-versa) can throw off detectors that expect an image to be either 100% real or 100% synthetic.
It's important to remember that no single tool is perfect. This is precisely why a multi-step verification process—combining traditional search, AI similarity search, and a dedicated detector—is so vital for feeling confident about an image's origin.
What Are the Privacy Implications of Uploading an Image?
When you upload a photo to an online service, you’re right to be cautious. The privacy implications of using an AI reverse image search can vary wildly from one platform to another, and knowing the difference is key.
Some of the big, general-purpose platforms might use the images you upload to train their own AI models. Your photo could get absorbed into a massive dataset, helping their system learn to recognize more objects, faces, or scenes. While your data is often anonymized, it’s still being used to build their commercial product.
On the other hand, privacy-focused tools are built differently from the ground up.
Tools like AI Image Detector are designed with a strict privacy-first philosophy. When you upload an image for analysis, it's processed in real-time and is never stored on our servers or added to any dataset. Once the analysis is done, the image is gone. Period.
This distinction is critical, especially for journalists handling sensitive photos, businesses verifying confidential documents, or frankly, anyone who doesn't want their personal pictures stored indefinitely without their consent. Always check a tool’s privacy policy before you upload anything.
How Can I Integrate AI Detection on My Website?
For businesses, developers, and platform moderators, manually checking every single user-uploaded image is just not realistic. The only way to combat fraud, misinformation, and inappropriate content at scale is to build automated detection right into your website or app. This is usually done with an Application Programming Interface (API).
Think of an API as a secure messenger between your platform and the AI detection service. Here’s a simple breakdown of how it works:
- User Uploads an Image: Someone on your site uploads a profile picture, a product photo, or any other image.
- API Call is Made: Your website's backend automatically sends that image to the detection service's API.
- Analysis is Performed: The service instantly analyzes the image for any signs of AI generation.
- Results are Returned: The API sends back a clear, simple result—usually a confidence score (e.g., "95% Likely AI-Generated") and other helpful data.
- Action is Taken: Based on that score, your platform can take automatic action, like flagging the image for human review, rejecting the upload, or limiting the user's account.
This automated process allows you to verify thousands of images per minute, creating a safer environment for your community without any manual work.
Ready to verify your images with confidence? AI Image Detector offers a free, private, and powerful tool to distinguish between human-made and AI-generated content in seconds. Try it now and see for yourself at https://aiimagedetector.com.



