How to Check If Photo Is Real: The Complete Guide
Knowing how to tell if a photo is real comes down to a few key techniques. You can start with a reverse image search to track down its origin, dig into its hidden EXIF data with a viewer to look for signs of tampering, or use a dedicated AI Image Detector to catch computer-generated fakes. When you combine these with a good old-fashioned visual inspection, you’ll have a powerful method for spotting fakes.
Why You Need to Know How to Verify a Photo

Have you ever scrolled past a photo so wild you had to do a double-take? Whether it’s an unbelievable nature shot or a shocking news event, the immediate question is: is this real? In a world filled with sophisticated AI and photoshop experts, being able to answer that question is a fundamental skill for navigating the internet.
Misinformation often travels at the speed of a share, and a single, powerful image is usually the vehicle. Pictures hit us on an emotional level long before our critical thinking kicks in, which makes them the perfect tool for manipulation. Learning how to check if a photo is real is your defense against being fooled.
The Detective’s Toolkit for Image Verification
This guide will walk you through the exact methods the pros use to separate authentic images from digital fakes. Forget guesswork; we’re focused on a repeatable process that gives you concrete evidence. No single technique is perfect, which is why we’ll combine several for a more reliable verdict.
Here’s what you’ll be able to do:
- Trace an image’s history online to find out where it first appeared and in what context.
- Examine its digital DNA (the metadata) for clues about the camera used and any subsequent edits.
- Spot the tell-tale visual signs of manual editing or AI generation that most people miss.
- Run it through modern tools built to detect the subtle fingerprints left behind by AI image generators.
The explosion in AI-generated imagery has raised the stakes. While it's exciting to see the creative possibilities of AI photography, it also means we have to be more vigilant than ever.
A truly critical eye doesn't just see what's in the photo; it questions how the photo came to be. This mindset is your first line of defense against visual misinformation.
Think of each section here as a new layer of your investigation. We'll start with the quickest checks and progressively move to more detailed analysis, giving you a complete workflow for verifying nearly any image you find.
Your Photo Verification Toolkit at a Glance
To give you a quick overview, here’s a breakdown of the core techniques we’ll be covering. Think of this as your cheat sheet for choosing the right tool for the job.
| Verification Method | Best For | Difficulty Level | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reverse Image Search | Finding an image's origin and first appearance. | Easy | Uncovers original source, date, and context. |
| Metadata (EXIF) Inspection | Checking for signs of editing or tampering. | Intermediate | Reveals camera details, software used, and timestamps. |
| Manual Visual Cues | Spotting obvious Photoshop or AI artifacts. | Easy-Intermediate | Identifies unnatural shadows, distorted lines, and AI errors. |
| AI Image Detector Tool | Detecting images created by AI generators. | Easy | Provides a probability score for AI generation. |
Each of these methods offers a different piece of the puzzle. By learning to use them together, you'll be well-equipped to make an informed judgment about a photo's authenticity.
Uncover a Photo's Origins with Reverse Image Search
When you're trying to figure out if a photo is legitimate, a reverse image search is almost always your first move. It’s a simple but powerful technique that flips the usual search process around. Instead of typing words to find a picture, you use the picture itself to find out where it's been on the internet. This is easily the quickest way to get a baseline read on a photo’s history.
Think about those "once-in-a-lifetime" wildlife photos that go viral. Before you hit share, a quick search can reveal if that same picture has been floating around for years, often with completely different backstories. This one action is your best first defense against old images being passed off as breaking news.
While Google Images is the go-to for many, it shouldn't be your only tool. For a deeper dive, several other search engines offer unique strengths that can give you much clearer, more specific results.
Go Beyond Google with Specialized Search Engines
Relying on a single search engine can give you blind spots. Different platforms crawl and index the web in their own way, so one might uncover a source that another completely misses. To do a proper job, you need to expand your toolkit.
- TinEye: I often start here because it’s built specifically for one thing: reverse image searching. Its killer feature is sorting results chronologically, which is invaluable for finding the oldest version of an image. This helps you nail down the first time a photo ever appeared online.
- Yandex: This Russian search engine has some seriously powerful image recognition tech under the hood. I've found it's often much better at finding visually similar images, even if they've been cropped or slightly altered. It can also be surprisingly good at identifying faces or landmarks within a photo.
- Bing Visual Search: Bing’s strength lies in identifying specific objects within a picture. It can pull up shopping links or related photos, which is great for verifying product images or identifying items in a scene to get more context.
Here’s a look at the TinEye interface. It's clean and straight to the point, designed to get you answers fast.

As you can see, the layout is all about its main function: upload an image and find out where and when it's been used before, so you can track it back to the original source.
How to Interpret Your Search Results
Getting a page full of results is the easy part. The real skill is in knowing how to read them. You're not just looking for matches; you're looking for clues about the photo's origin, history, and context. A ton of results usually just means an image is popular. The important details are hidden in the dates and sources.
The context in which a photo is presented is just as important as the image itself. A reverse image search reveals how that context has shifted over time, exposing where the narrative may have been twisted.
Hunt for the earliest indexed date. If a photo claiming to be from a protest last week shows up on a blog from 2015, that’s a massive red flag. Also, check the image resolution. The original source is almost always the highest-quality version out there. Copies tend to get fuzzy and pixelated as they’re saved and re-uploaded over and over.
For example, a politically charged image might be shared as "proof" of a recent event. A reverse search could trace it back to a stock photo site or a news story from a different country five years ago. This doesn't just show the context is wrong—it proves someone is trying to mislead you.
Here's a pro tip from my own experience: crop the image. If you're suspicious of a specific person or object in a busy photo, crop down to just that element and search again. This focused approach can sometimes uncover the original, separate images that were stitched together to create the fake.
Dig Into a Photo's Digital Fingerprint with Metadata
Every digital photo you see carries a hidden layer of information, a sort of digital fingerprint. It's called metadata, and the most common type for images is EXIF data (Exchangeable Image File Format). This data is automatically embedded by the camera or smartphone the instant a picture is snapped.
Think of it as the photo's technical backstory. It’s one of the best ways to check if a photo is real because it provides a trail of evidence that's much harder to tamper with than the pixels themselves.
This digital fingerprint can be surprisingly detailed. You can often find the exact camera make and model (like an Apple iPhone 14 Pro), the lens used, and even precise settings like shutter speed, aperture, and ISO. For anyone trying to verify an image, this is pure gold.
There's one catch, though. Social media platforms like Instagram and Twitter usually strip this data from photos when they're uploaded to protect user privacy. So, this method works best when you have the original file, which you're more likely to get from a news source, a direct email, or a personal blog.
How to Uncover the Hidden Data
Getting to this metadata is simpler than you might expect. In fact, your computer has everything you need to start.
- On a Windows PC, just right-click the image file, select Properties, and then navigate to the Details tab.
- On a Mac, open the photo in Preview, then go to Tools > Show Inspector.
If you want a more powerful look, there are some great free online tools. I often recommend Jeffrey's EXIF Viewer because it digs deeper than the basic viewers on your computer and lays everything out in an easy-to-read format. All you have to do is upload the image file or paste its URL.
Here's a peek at the kind of information it can pull up.
As you can see, the output can show you everything from the exact time the photo was taken (down to the second) to the camera model and whether the flash went off. These are the kinds of clues that can either back up a photo's story or expose it as a fake.
Spotting the Red Flags in Metadata
So, what are you actually looking for? The main goal is to hunt for contradictions.
For instance, if someone claims a photo is from a protest that happened yesterday, but the creation date in the metadata is from five years ago, you’ve got a problem. The same goes for location. If the embedded GPS coordinates place the photo in a different country, that's a massive red flag.
The real smoking gun is often found in the "Software" or "Image-Processing" fields. If you see a program name like "Adobe Photoshop" listed here, you have direct proof the image was edited. While not every edit is a malicious fake, it confirms the photo is no longer the raw, original shot.
Here’s a quick checklist of things to watch for:
- Missing Data: If an image file has zero EXIF data, be suspicious. This is especially true if the source claims it's an original, untouched photo. It could mean someone intentionally scrubbed the data.
- Creation Date vs. Context: Does the timestamp make sense for the event being shown?
- Editing Software: The mention of software like Photoshop or GIMP is a dead giveaway that the image has been altered.
- GPS Mismatch: If location data is included, does it match where the photo was supposedly taken?
By analyzing a photo's metadata, you're adding a layer of forensic investigation to your fact-checking. It takes you beyond what your eyes can see and gives you a powerful tool for finding the truth.
Train Your Eyes to Spot Signs of Manipulation

Sometimes, the best tool you have to check if a photo is real is your own intuition. While technology is great, sophisticated fakes often have subtle visual mistakes that just feel off. Learning to trust that gut feeling and then actively look for the evidence is a crucial skill for anyone trying to sort fact from fiction.
Even the most advanced fakes can struggle to replicate the basic laws of physics, especially the way light and shadow work in the real world. This is often where the whole illusion falls apart.
Follow the Light and Shadows
In any genuine photo, the light has to come from somewhere. That means every shadow cast by every object should be consistent with that single light source. When you see shadows pointing in different directions, that’s a massive red flag.
Think about a simple outdoor photo taken on a sunny day.
- Shadow Direction: All shadows should fall away from the sun. If one person's shadow points left while a nearby tree's shadow points right, you're almost certainly looking at a composite image.
- Shadow Hardness: Bright, direct sunlight creates sharp, well-defined shadows. Overcast days or shady spots produce soft, blurry shadows. A mix of hard and soft shadows in the same lighting condition just doesn't happen.
Here’s a pro tip: zoom in on people's eyes. The tiny reflections of light sources, known as catchlights, should look the same for everyone in the shot. If one person has a round catchlight and another has a square one, it could mean one of them was digitally added.
Our brains are wired to notice when faces and physics look wrong. If you get an initial feeling that something isn’t quite right, lean into it. That instinct is often the first clue that an image has been manipulated.
Scrutinize the Edges and Perspectives
Pasting an object into a new background is tricky, and the edges are where mistakes are usually made. Get used to zooming in on the outlines of people and objects. Look for blurry or jagged lines, a slight halo or glow, or edges that seem unnaturally sharp compared to the rest of the image. These are classic signs of a sloppy Photoshop job.
Perspective is another big one. In the real world, parallel lines like the sides of a road or the top and bottom of a building appear to converge at a distant vanishing point. If objects in a photo defy this rule—like a person who seems way too big for the room they're standing in—the image is likely fake.
The Uncanny Valley of AI Fakes
AI-generated images have their own unique brand of weirdness. The algorithms are getting smarter, but they still get tripped up by certain details.
Keep an eye out for these common AI flaws:
- Hands and Fingers: AI notoriously struggles with hands. You might see people with six fingers, twisted knuckles, or hands that seem to melt into the background.
- Teeth and Eyes: Look for teeth that are unnervingly perfect or rows that don't quite line up. Eyes might have mismatched pupils or strange, non-human reflections.
- Background Gibberish: Check the background for text on signs that looks like a made-up language, patterns on wallpaper that warp illogically, or objects that blend into each other.
These AI quirks are becoming rarer, but they haven't disappeared. As deepfakes become more convincing, other verification methods are gaining importance. For instance, the rise of AI manipulation has spurred the adoption of biometric security. As of 2023, over 176 million Americans were already using facial recognition for identity verification, showing just how critical robust authentication has become. You can find more insights on the connection between biometrics and security on photoaid.com.
Bring in the AI: Using Advanced Image Detection Tools
When your own eyes and a metadata check still leave you scratching your head, it’s time to fight fire with fire. Or in this case, fight AI with AI. Specialized AI image detectors are built to spot the incredibly subtle, mathematical fingerprints that generative models leave behind—clues that are often completely invisible to us. These tools are the heavy hitters when you need to check if a photo is real.
Unlike a person, who might look for wonky shadows or an extra finger, these tools go straight to the pixel level. They’re hunting for tell-tale patterns in digital noise, weird textural inconsistencies, and other artifacts that basically scream "I was made by a machine." You'll typically get back a probability score, which can be a huge help in confirming your suspicions.
But let's be realistic. These tools aren't magic, and they aren't infallible.
The Good, the Bad, and the AI Detector
The real power of an AI detector is its ability to see what we can't. It can flag digital artifacts in a photo that looks absolutely perfect, making it a critical partner in the verification game, especially as AI fakes get scarily good. To get a better sense of how this all works under the hood, we break down the technology in our guide to the AI photo analyzer.
Now for the catch. These detectors can get it wrong. Sometimes they'll produce a false positive, flagging a heavily compressed or edited photo as AI-generated when it’s perfectly real. On the flip side, they can be outsmarted by brand-new AI models they haven't been trained on yet.
Think of an AI detector as an expert consultant, not the final judge. It gives you a powerful piece of evidence, but that evidence should always be weighed against what you found from a reverse image search and any metadata you could pull.
This simple workflow shows how to blend AI analysis with human common sense.
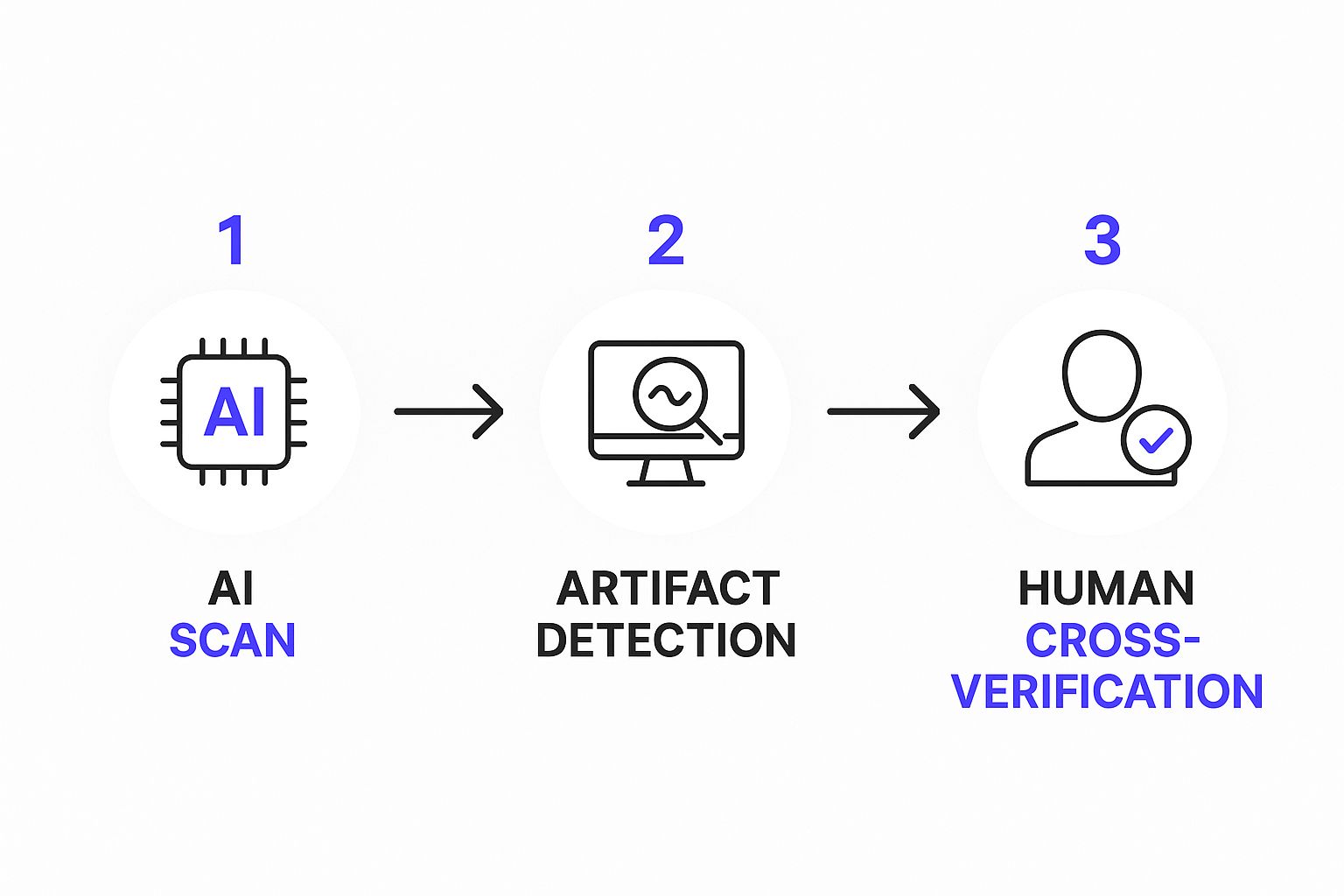
The takeaway is clear: the AI scan is a crucial middle step, but your own brain is still the most important tool for interpreting the results.
How to Fit AI Detection Into Your Process
So, when do you actually use one of these tools? The best time is after you've already done the basics. If a reverse image search comes up totally empty and the metadata has been wiped clean, an AI detector is your logical next move to see if the image is synthetic.
Here are a few real-world situations where an AI detector is a lifesaver:
- Checking social media profiles: Is that person who just followed you real, or is their profile picture a computer-generated face?
- Vetting user-submitted content: If you run a platform or marketplace, you need to know if product photos or user uploads are authentic to maintain trust.
- Analyzing breaking news images: When a shocking photo pops up out of nowhere with no clear source, an AI scan can be a quick first-pass to gauge its legitimacy.
It's worth noting that even the biggest AI platforms can stumble here. A study from the Tow Center for Digital Journalism found that out of 280 queries sent to seven major AI systems, only 14 gave accurate photo verification results. You can read more about the challenges in this insightful report on photo verification. This just drives home the point: use specialized detectors and never rely on just one method.
Putting It All Together: A Practical Verification Workflow
When you come across an image that just doesn't feel right, your job is to build a solid case for or against its authenticity. Real confidence doesn't come from a single tool or a quick glance; it’s about piecing together clues from different angles.
The golden rule is simple: never trust just one verification method. A photo with scrubbed metadata isn't automatically fake, just as a flag from an AI detector doesn't instantly confirm it. Each technique gives you one piece of a much larger puzzle. It's when all the pieces start pointing in the same direction that you can make a truly informed decision.
A Layered Approach to Verification
To work efficiently, start with the broadest and quickest checks first, then gradually dig deeper as you gather more evidence. This stops you from getting tunnel vision and jumping to a conclusion too early.
Here’s a practical sequence I follow:
First, run a reverse image search. This is your wide-net approach. Use a few different engines like TinEye and Yandex to hunt for the image's origin. The goal here is to find the very first time it appeared online, which gives you its original context and date.
Next, trust your own eyes. It's time for a close-up manual inspection. Zoom way in. Are the shadows falling in the right direction? Do you see any blurry edges where things have been pasted together? Look for the classic AI giveaways—things like six-fingered hands, distorted text in the background, or textures that look just a little too perfect.
Then, dig into the metadata. If you have access to the original file, its EXIF data is a potential goldmine. Check for timestamps that don't line up with the claimed story, GPS coordinates in an impossible location, or clear signs of editing software like Adobe Photoshop.
Finally, use an AI detector. Think of this as your final technical confirmation, especially when the other methods don't give you a clear answer. An AI scan can often spot the subtle digital fingerprints of AI generation that are completely invisible to the human eye. If you want to dive deeper into how these tools work, it's worth understanding the accuracy of AI detectors and what their results really mean.
This layered process builds a much stronger foundation for your conclusion. With the rise of deepfakes, this kind of cross-verification isn't just a good idea—it's essential. Governments are catching on, too. As of 2025, major legislation like the EU AI Act and the UK Online Safety Act aims to fight deepfakes by demanding clear labels and the removal of harmful manipulated media. You can get up to speed on these deepfake statistics and legal responses on deepstrike.io.
By combining these techniques, you transform from a passive viewer into an active digital investigator. This critical mindset is your best defense in a world where seeing isn't always believing.
Ready to put your new skills into practice? Start analyzing images with the confidence of an expert. Use the AI Image Detector for a free, instant scan. Check your first image now at aiimagedetector.com and discover the story behind the pixels.


