How to Spot a Real Fake Photo in a Digital World
You've probably heard the term "real fake photo" floating around. It’s a synthetically generated image, often cooked up by AI, that’s designed to look completely authentic. These images are masters of disguise, blurring the lines between what’s real and what’s not. As the tech gets smarter, a quick glance just isn't enough anymore.
The New Reality of Digital Images

Welcome to an age where seeing isn’t always believing. The explosion of powerful AI tools like Midjourney and DALL-E has put the power to create a convincing real fake photo into just about anyone’s hands. What used to take a photoshop expert hours of meticulous work can now be done in seconds, flooding our feeds with hyper-realistic scenes that never actually happened.
This guide is your field manual for navigating this new reality. We’ll cover everything from simple visual tells you can spot yourself to the advanced AI detectors the pros use. This isn't just for tech experts; it's essential for everyone.
- Journalists need to vet their sources to protect their credibility.
- Educators have to equip students with critical digital literacy skills.
- All of us need to shield ourselves from a constant stream of misinformation.
Think of this as your crash course in visual truth. By the end, you'll have a reliable process to question, analyze, and ultimately uncover the real story behind any image you come across.
The Scale of the Challenge
The sheer volume of AI-generated content is staggering. The AI image generator market is on a rocket ship, projected to grow from USD 9.10 billion in 2024 to a massive USD 63.29 billion by 2030. That financial boom means billions of "real" fake photos are pouring into our social media and news feeds every single day.
Remember the viral "Pope in a Puffer Jacket" image from 2023? That fake photo racked up over 8 million views on X (formerly Twitter) before anyone called it out. It’s a perfect example of how this content spreads like wildfire—reportedly six times faster than real news.
This isn't just about spotting funny fakes. It's about building a fundamental skill for modern life: the ability to tell reality from sophisticated fabrication. The stakes are high, with real-world consequences for everything from public opinion to personal security.
Understanding the Technology Behind the Fakes
To get good at spotting a real fake photo, it helps to know what you’re up against. These images fall under the bigger umbrella of synthetic media, a term for any content generated or altered by AI.
If you want to go deeper, our guide on synthetic media is a great place to start. A little foundational knowledge goes a long way in helping you recognize the subtle but distinct fingerprints that AI models tend to leave behind.
Spotting Fakes with Your Own Eyes

Before you even think about firing up any software, remember that your own eyes are your best starting tool. Learning to visually inspect an image is the fundamental first step in spotting a fake. AI models, for all their power, are notorious for leaving behind subtle clues that a careful observer can catch.
This first pass is really about cultivating an instinct for what just looks "off." It’s a skill that's part common sense, part forensic curiosity. If you know what to look for, you can often flag a synthetic image in seconds, long before needing more technical tools.
Checking the Human Element
AI generators have gotten shockingly good at creating human faces, but they still get tripped up on the tiny details that make us look... well, human. This is usually where you'll find the most glaring mistakes.
Start with the eyes. AI-generated eyes can look glassy, dead, or have reflections that are just a little too perfect and don't match the light source in the scene. Zoom in on the pupils—are they perfectly round, or do they have odd shapes?
Next, look at the skin. AI often generates skin that's unnaturally smooth, missing the pores, tiny blemishes, and fine lines that even a heavily airbrushed photo would have. It can sometimes have a waxy or plastic-like sheen that just feels wrong.
And then there's the classic AI giveaway: hands. Seriously, always check the hands. Count the fingers. Look for weird anatomy, like extra joints, fingers that seem to melt into each other, or hands bent at impossible angles. While the newer models are getting better, hands are still a major weak spot.
A convincing image has to get every single detail right, from the subtle sag of skin to the natural lopsidedness of a smile. A fake only needs to get one of these things wrong to give itself away.
Scrutinizing the Scene and Its Physics
Look beyond the people in the photo; the environment itself is packed with clues. A fake photo often starts to unravel when you apply some basic real-world physics.
Keep an eye out for inconsistencies in:
- Shadows and Lighting: Are all the shadows pointing in the same direction, consistent with a single light source? Does the light on a person actually match the ambient light in the background? Mismatched lighting is a dead giveaway that elements were slapped together or generated separately.
- Reflections: Check any reflective surface you can find—windows, mirrors, even the glint on a pair of sunglasses. Do the reflections show what they're supposed to show? AI often fumbles here, creating blurry messes or nonsensical scenes that don't line up.
- Textures and Patterns: Get in close on things like clothing fabric, wood grain, or a brick wall. AI can sometimes create patterns that repeat in an unnatural way or textures that just look flat and lack realistic detail. That infamous image of the Pope in a puffer jacket? The fabric had a weird, overly smooth quality that screamed "fake."
We understand these physical laws instinctively, but they're incredibly complex rules for an AI to replicate perfectly every single time. A shadow that defies the sun is all the proof you need.
Analyzing the Uncanny Details
The last part of your visual check is to hunt for the truly bizarre artifacts—the little illogical details that no human artist or photographer would ever create.
Take a look at the background. Is there any text on signs or buildings? Can you actually read it, or is it just a jumble of characters that look like letters but don't form real words? This kind of "pseudo-text" is a classic sign of AI generation.
Also, examine how objects interact with each other. Do eyeglasses sit properly on someone's face, or do the arms seem to merge into their hair? Do earrings or necklaces look right, or are they bizarrely blended with the skin? These small, illogical flaws are often the clearest fingerprints an algorithm leaves behind. It's a sign of a system that understands pixels, but not the real-world logic that governs them.
Uncovering an Image's Digital Footprint
Once you’ve given an image a good, hard look with your own eyes, it’s time to dig into its digital history. Every photo file carries a trail of data, and learning to read that trail can instantly confirm or bust your suspicions. This is where we shift from simple observation to a bit of digital forensics.
Think of it this way: a reverse image search is like checking an online package's tracking history to see every stop it made. Checking its metadata, on the other hand, is like opening the box to read the original shipping label. Both are absolutely essential for spotting a fake.
Harnessing the Power of Reverse Image Search
A reverse image search is your first and most powerful technical tool. Instead of typing in words, you upload the image itself, and engines like Google Images or TinEye scour the web for matches.
But you’re not just looking for a simple match. You're digging for context and origin.
- Find the Original Source: A reverse search can often lead you to the very first time an image was indexed online. Was it on a legitimate news site, a personal blog, or a stock photo library? The source tells you a lot.
- Identify Alterations: You’ll probably find different versions of the photo. Seeing the original before it was cropped, color-corrected, or photoshopped can instantly expose a fake.
- Uncover Misleading Context: A real photo can be used to tell a completely fake story. I’ve seen it countless times—an image from a protest years ago suddenly gets passed off as a current event. A reverse search will show you the picture's true context.
A reverse image search is less about finding a perfect match and more about building a timeline. The oldest, highest-resolution version you can find is almost always the original. If your "breaking news" photo first appeared on a satire site five years ago, well, there’s your answer.
Demystifying Image Metadata
Every time you snap a photo with a modern camera or phone, a whole bunch of data gets embedded right into the file. This is called EXIF data (Exchangeable Image File Format), and for an investigator, it’s a goldmine.
This hidden data can tell you the exact camera model used, the date and time the photo was taken, and even the precise GPS coordinates of where it was shot. It provides a powerful, factual baseline for any authentic photo. If you want to get into the nitty-gritty, you can check out our guide on how to check the metadata of a photo.
The presence—or absence—of this data is a massive clue.
Reading the Clues in EXIF Data
An authentic photo, straight from a camera, is usually packed with EXIF data. A real fake photo generated by an AI model, on the other hand, will have none. It was never taken by a physical camera, so it has no creation date, no GPS location, and no camera settings to record. It’s a digital ghost.
Social media platforms like Instagram and X often strip this data to protect user privacy, so a lack of metadata isn't always a smoking gun. However, when you're examining a file that claims to be a raw, unedited image from a source, missing data is a huge red flag.
For example, a photographer was able to debunk a viral photo of a giant moon behind an arch. How? He checked the metadata. It showed the image was taken on a day when the moon was just a tiny crescent on the opposite horizon. The EXIF data proved the scene was a composite, not an incredible feat of photography.
Comparing Image Verification Tools
When you're ready to start digging into the technical side, you'll find a handful of fantastic, free tools. Each has its strengths, and knowing which one to use can save you a lot of time. Here’s a quick rundown of some of my go-to options.
| Tool Name | Primary Function | Key Feature | When to Use It |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Images | Reverse Image Search | Massive, constantly updated index of the web. | Your first stop for finding duplicates, origins, and different contexts of an image. |
| TinEye | Reverse Image Search | Sorts results by date, making it easy to find the oldest version. | Excellent for establishing an image’s timeline and finding the original source. |
| FotoForensics | Error Level Analysis (ELA) | Highlights parts of an image with different compression levels, revealing potential edits. | When you suspect a photo has been photoshopped but the edits are too subtle to see. |
| EXIF Data Viewer | Metadata Analysis | Reads and displays all the hidden EXIF data embedded in a photo file. | When you have the original file and need to verify its camera source, date, or location. |
Each of these tools offers a different lens to view the image through. I usually start with a broad reverse search on Google and TinEye, then move to EXIF data if I have the original file, and finally use FotoForensics if I still suspect manipulation.
The technology behind this is growing fast. The image recognition market, which powers these tools, is projected to hit USD 163.75 billion by 2032, according to Fortune Business Insights. This investment is already paying off—Reuters developed a verification toolkit that caught 89% of AI fakes, slashing debunking time from days to minutes. That's a game-changer when you consider that an estimated 15% of images on social platforms are AI-generated and misinformation spreads 70% faster than the truth.
Using AI to Detect AI Images
So, you’ve done the visual check and a reverse image search turned up nothing. What’s next? When the human eye just can't spot the trickery, it’s time to fight fire with fire. Our best ally against synthetic media is often AI itself, specifically in the form of specialized AI image detectors.
These tools don’t see an image the way we do. They’re trained on massive datasets of real and AI-generated pictures, learning to pick up on the invisible artifacts and statistical quirks that generation models leave behind. We're talking about pixel-level inconsistencies and digital noise patterns that are completely lost on us.
How AI Image Detectors Work
Think of an AI detector as a digital forensics specialist. It scans the image file for the subtle, tell-tale signs left behind during the creation process.
It’s hunting for things like:
- Pixel Inconsistencies: AI models sometimes create an unnatural smoothness or weird repeating patterns where there should be random texture, like in a clear sky or on skin.
- Compression Artifacts: It analyzes how the image was saved and compressed, looking for signatures more common in algorithmically generated files than in photos from a real camera.
- Algorithmic Fingerprints: Every AI model—whether it's Midjourney, DALL-E, or Stable Diffusion—has its own unique "style" for building an image. These subtle digital fingerprints can often be identified by a detector trained to look for them.
This process gives you a fast, objective analysis when your gut feeling isn't enough to go on. It’s about moving past a hunch and getting a quantifiable assessment.
A Practical Guide to Using a Detector
Most AI image detectors are designed to be pretty straightforward. The real skill isn't just uploading the file; it's in knowing how to read the results.
First, you upload the image. It’s usually a simple drag-and-drop interface that accepts common file types like JPEG, PNG, or WebP. The analysis starts right away.
Next, you review the confidence score. Instead of a simple "yes" or "no," you'll typically see a percentage or a scale ranging from "Likely Human" to "Likely AI-Generated." This number reflects how certain the tool's model is about its conclusion.
Finally, examine the detailed report. The best tools don't just give you a score—they show their work. They might provide a heatmap that highlights the specific areas of the image that screamed "AI!" This kind of visual evidence is invaluable for backing up the tool's verdict.
For anyone wanting to see what these reports look like in action, our own AI Image Detector is a great place to start. That level of detail is exactly what you need to make an informed decision, especially if you're a journalist or moderator.
The goal isn't just to get a verdict but to understand why the verdict was reached. A high AI score on an image with perfect hands might be due to a synthetically generated background, a detail the report would help you identify.
Interpreting the Results Like a Pro
A confidence score is a powerful piece of evidence, but it needs context. A result of "95% Likely AI-Generated" is a pretty clear signal. But what about a score of "60% Likely AI-Generated" on a photo that’s been heavily edited? That requires more critical thinking.
This is where your earlier detective work—the visual inspection and reverse image search—comes back into play. Does the AI detector’s finding line up with everything else you found? If you noticed odd-looking hands and the detector flags the image as AI, you’ve built a solid case.
But if a reverse search traces the photo back to a reputable news site from 10 years ago and the detector still gives it a moderate AI score, it could be a false positive triggered by digital restoration or heavy-handed editing, not a full-blown fake.
The AI detector market is booming, and for good reason—it's projected to hit USD 2.06 billion by 2030. With deepfake images having spiked an incredible 550% since 2022 and 90% of them used maliciously, the need for reliable verification is urgent. In a real-world example of this, platforms like eBay reportedly blocked 1.2 million AI-driven listings in 2025 by using these tools to scan files in seconds, saving thousands of hours of manual review.
To get a better handle on how this technology is reshaping media, it's worth exploring broader discussions on the role of AI in newsrooms. Understanding this context helps professionals grasp the full implications. Ultimately, an AI detector is a powerful final step in your verification workflow, providing the technical evidence you need to make a confident call.
Building Your Professional Verification Workflow
Just knowing a few tricks isn't enough. To confidently tell a real photo from a fake one, especially when the stakes are high, you need a repeatable process. Winging it with ad-hoc checks is a recipe for mistakes, particularly when you're on a deadline or up against a sophisticated fake.
A professional workflow isn't just for journalists or fact-checkers. It’s a solid framework for anyone who needs to be sure about an image before they hit "share." It’s about building a mental checklist that becomes second nature, turning a gut feeling into a clear, evidence-based conclusion. Let's walk through how to build one.
The Triage: Your First Look
Your process should always start with a quick, critical look at the image itself. This is your triage stage. Before you fire up any fancy tools, just use your eyes and ask the basic questions we covered earlier.
Do the hands and eyes look natural? Are the shadows falling correctly? Is there any garbled, nonsensical text in the background? This initial once-over often gives you an immediate answer—blatant AI errors like six-fingered hands are a dead giveaway. If not, it helps you zero in on specific oddities to investigate further.
Escalation One: Chasing the Digital Footprint
If an image passes that initial eye test, it's time to dig into its digital history. This is where you bring in the tools to find out where it came from and what story its data tells.
Kick things off with a reverse image search on multiple engines, like Google Images and TinEye. You’re not just looking for copies; you're on the hunt for the oldest, highest-quality version to find its original context. If the photo first appeared on a reputable news site five years ago, that’s a great sign. If it only exists on brand-new, anonymous social media profiles, your suspicion should be high.
At the same time, if you have what claims to be the original file, check its EXIF data.
- Data Present? Real photos usually contain data about the camera model, date, time, and sometimes even GPS coordinates.
- Data Absent? AI-generated images have no EXIF data because a camera never took them. A completely blank slate is a huge red flag.
- Data Conflicting? Does the timestamp or location directly contradict the story being told about the photo? That's a smoking gun.
A journalist once debunked a viral photo of a supposed supermoon behind a famous arch by simply checking its metadata. The data showed the photo was taken on a day when the moon was just a tiny crescent on the opposite side of the sky. The image was a composite.
This whole process can be simplified, especially when you bring in a dedicated tool.
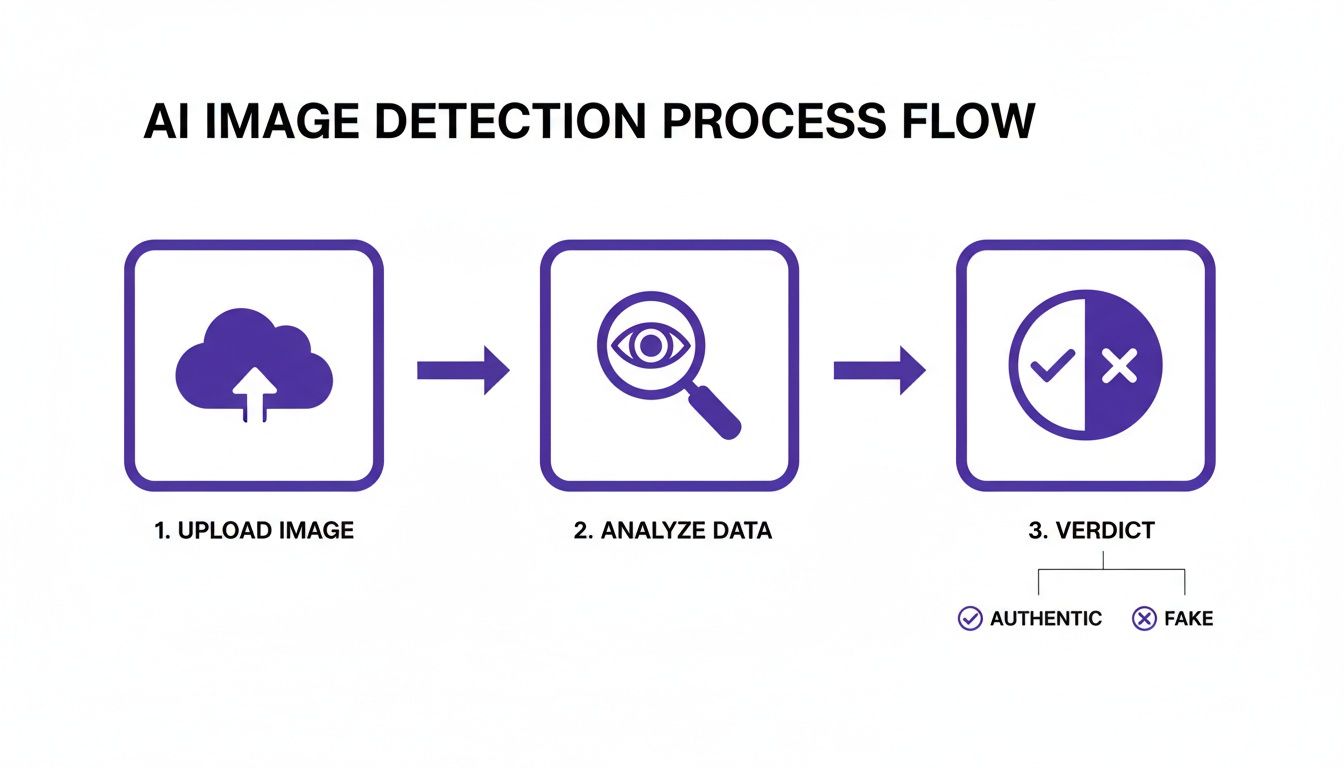
It really boils down to a simple sequence: you upload the image, the tool analyzes it at a pixel level, and you get a clear verdict.
Escalation Two: The AI Detector's Verdict
So, what happens when a reverse image search comes up empty and the metadata is missing? You're likely looking at a brand-new creation. This is precisely when you turn to an AI image detector.
This is your final, most powerful move. Upload the image and carefully review the results. Don't just glance at the final score—look for detailed reports or heatmaps. These visuals can pinpoint the exact areas the algorithm found suspicious, giving you powerful evidence to support its conclusion. An AI detector is designed to spot the subtle, almost invisible artifacts that even the newest AI models leave behind.
To get even better at this, it helps to understand how these images are born. Learning what is prompt engineering—the art of giving instructions to an AI—can give you incredible insight into why generated images have the flaws they do.
By weaving these three phases together—visual triage, digital footprinting, and AI detection—you build a rock-solid and defensible workflow. You're no longer guessing; you have a clear path to verify any real fake photo that comes your way.
Common Questions Answered
When you're trying to figure out if an image is real or AI-generated, a few tricky situations always seem to pop up. Here’s how I think about navigating some of the most common ones.
Can AI Detectors Keep Up with Newer AI Models?
It’s a constant cat-and-mouse game, and the answer is yes, for the most part. The best detection tools aren't just looking for the signature of one specific AI model like Midjourney v5 versus v6. Instead, they're trained to spot the fundamental artifacts and statistical oddities that are inherent to the AI generation process itself.
No detector will ever be 100% foolproof, that’s just a fact. But a good one gives you a reliable confidence score—a statistical edge that's far better than relying on your eyes alone. It's an essential piece of the puzzle in any serious verification workflow today.
What if a Reverse Image Search and an AI Detector Give Me Conflicting Results?
When your tools disagree, don't get frustrated. That's actually a huge clue telling you to dig deeper. This isn't a dead end; it’s a signpost.
Let’s break down what this conflict usually means:
- No reverse search results, but a high AI score: This is a classic sign of a brand-new AI creation. It hasn’t been shared enough to be indexed by search engines, making it a prime suspect for an original real fake photo.
- Legitimate sources found, but a high AI score: This one is trickier. It often means a real, authentic photo was taken and then heavily altered with AI tools. Think of a real news photo where a person or object was digitally added or removed. The base is real, but key parts are fake.
When your tools give you conflicting information, don't just pick the one you like better. That conflict is your cue. Scrutinize the AI detector's detailed report, evaluate the credibility of the sources from your reverse search, and consider that you might be looking at a hybrid image—part real, part AI.
Are There Legal Dangers in Using AI-Generated Images?
Absolutely. The legal and ethical ground is still shifting, but there are definite risks you need to be aware of. Ethically, the most important rule is transparency. If you're using an AI image, you need to disclose it. Passing it off as real is where you get into trouble.
Legally, things get complicated, especially with copyright. In many places, it's a huge gray area. If an AI model was trained on copyrighted photos, the images it generates could put you at risk for an infringement claim. Always read the terms of service for the AI tool you're using, and if it’s for a commercial project, it's smart to talk to a legal expert.
How Do I Tell the Difference Between Heavy Photoshop Editing and AI Generation?
This is probably one of the toughest calls to make, and it takes a trained eye. A photo that's been heavily edited in a program like Adobe Photoshop still has the DNA of a real photograph. The core pixels, lighting physics, and metadata usually trace back to a camera. The edits might be drastic—smoothing skin, changing colors—but the foundation is real.
A true real fake photo, on the other hand, is built from the ground up by an algorithm. It leaves behind its own unique fingerprints: that signature waxy or overly smooth skin, bizarre details in the background that defy logic, or strange, repeating patterns. AI detectors are built specifically to find these synthetic markers, which is why a heavily edited photo might be flagged as "Human" or "Mixed," while a purely generated one gets a clear "AI" verdict.
Ready to stop guessing? With AI Image Detector, you get a clear, fast, and reliable verdict on any image. Our models cut through the noise in seconds, giving you the confidence to tell authentic photos from AI fakes. Try AI Image Detector for free today.



