A Guide to Deep Fake Detection Tools and Techniques
Deepfake detection is all about using technology to figure out if a video, image, or audio file is a synthetic forgery created by artificial intelligence. These tools are trained to spot the tiny, digital fingerprints and subtle inconsistencies that AI models leave behind—flaws that are almost always invisible to the naked eye but give away the content's artificial origin. In a world flooded with fake content, this has become an essential tool for fighting back against misinformation and fraud.
What Are Deepfakes and Why Do They Matter

Think of a deepfake as a high-tech digital puppet. It uses a type of AI called deep learning to generate stunningly realistic—but entirely fake—media. The technology can do incredible things, like seamlessly grafting one person's face onto another's in a video, perfectly cloning a voice from just a few seconds of audio, or creating photorealistic images of people and places that don't even exist.
What started as a niche experiment has quickly become a mainstream problem with serious consequences. The real danger of deepfakes is how they systematically dismantle trust. When we can no longer be sure if what we’re seeing and hearing is real, the very pillars of journalism, legal evidence, and public conversation start to crack.
The Real-World Impact of Synthetic Media
This isn't some far-off, futuristic threat. It's happening right now, and the problem is getting worse. Malicious deepfakes are being used for all sorts of alarming purposes, affecting everything from our personal safety to international politics. This explosion in deceptive media has, in turn, created a massive need for tools that can reliably verify what’s real.
The market reflects this urgency. The global deepfake detection industry is expected to grow at a compound annual rate of 37.45% between 2023 and 2033, according to a report from Spherical Insights. This growth is driven by a simple, pressing need: protecting society from increasingly sophisticated digital fraud.
Here are just a few of the most critical risks we face:
- Political Misinformation: Imagine a fake video of a world leader declaring war or a candidate confessing to a crime they never committed. This kind of content can easily sway elections, spark social unrest, and destabilize governments.
- Financial Fraud: Scammers are now using AI voice-cloning to impersonate company executives over the phone, tricking employees into making massive, unauthorized wire transfers. This is often called "vishing," or voice phishing.
- Personal Harassment: Deepfakes are used to create non-consensual explicit material targeting individuals, causing immense emotional trauma and lasting damage to their reputations.
- Erosion of Media Trust: As people become more aware of fakes, they might start disbelieving authentic news and evidence. This "liar's dividend" makes it incredibly difficult for journalists and fact-checkers to combat actual misinformation.
The ultimate goal of a deepfake isn't just to fool one person. It's to create an environment of uncertainty where people begin to doubt everything, making it easier for misinformation to spread unchallenged.
This escalating threat makes deepfake detection a non-negotiable skill for anyone working in media, education, finance, or security. Knowing how to spot a deepfake is our first line of defense. By learning the red flags and using the right tools, we can start to push back and restore confidence in the digital world.
How Deepfake Detection Actually Works
To the naked eye, a really good deepfake is often indistinguishable from reality. So, how does a machine spot a forgery that we so easily miss? It all comes down to hunting for microscopic clues and digital “fingerprints” that AI models leave behind when they create something.
Think of a deepfake generator like an art forger trying to pass off a replica as a masterpiece. It might look perfect from a few feet away, but a trained expert can spot tiny inconsistencies—in the brushstrokes, the paint chemistry, or even how the canvas has aged. Deepfake detection technology works on the same principle, acting as a digital forensic expert trained to find those subtle flaws.
It isn't magic; it's just a highly refined process of pattern recognition. The algorithms are fed enormous datasets with thousands of hours of real video and millions of authentic images, alongside an equally massive library of known deepfakes. This process teaches the system to recognize the baseline for what’s “normal” and what just feels… off.
Uncovering Digital Artifacts and Inconsistencies
At the heart of most detection methods is an analysis of common AI-generated artifacts. These are the subtle giveaways that pop up because AI models, for all their power, don't yet have a true grasp of the complex physics and biology of the real world. They're essentially making an educated guess at how things should look.
Detection models scrutinize every pixel for clues, looking for things like:
- Unnatural Blinking: Early deepfakes were notorious for featuring people who rarely, if ever, blinked. Newer models have gotten better, but they still often struggle to replicate the natural, subconscious rhythm of human blinking.
- Inconsistent Lighting and Reflections: An AI might render a face perfectly but completely fail to match the lighting on that face to the surrounding environment. You'll see things like distorted or missing reflections in a person's eyeglasses or pupils.
- Pixel-Level Anomalies: The process of digitally grafting a face onto a video can leave behind bizarre artifacts, especially around the edges where the synthetic face meets the real background. This can show up as weird blurring, odd color mismatches, or an unnatural smoothness.
At its core, deepfake detection exploits the gap between what an AI simulates and what actually happens in physical reality. The technology is trained to find the exact points where that simulation breaks down, even if the flaw is totally invisible to us.
Analyzing Biological and Physical Signals
Beyond just looking for visual artifacts, more advanced systems search for subtle biological and physical signals that are incredibly difficult for an AI to fake convincingly. These methods go beyond just looking at the image and instead analyze the underlying motion and physiology being shown.
This approach is like a detective watching a suspect's body language for tells, rather than just listening to their story. The system is essentially asking: does this person move and behave like a real human being?
Common signals include:
- Heart Rate Analysis: It might sound like science fiction, but imperceptible changes in skin color on a person's face actually correspond to their blood flow and pulse. Specialized tools can analyze these tiny color fluctuations to see if a biological heartbeat is even present. Most AI generators don't bother simulating something this complex.
- Head and Body Movements: Humans have unique, slightly imperfect ways of moving their heads and bodies. AI-generated movements can sometimes appear way too smooth, too jerky, or just physically awkward in a way that defies natural anatomy.
- Facial Expression Transitions: The way our facial muscles shift between expressions—from a smile to a frown, for example—is incredibly nuanced. Deepfakes might create flawless individual expressions but often fail to generate smooth, believable transitions between them.
By combining these different analytical techniques, a robust deepfake detection tool builds a comprehensive case for or against a piece of media's authenticity. To get a better sense of how these systems fit together, you can learn more about the mechanics of a fake detector machine and its core architecture. This multi-layered approach is our best defense, ensuring that even as deepfakes get more realistic, we can still find the digital breadcrumbs they leave behind.
Integrating Media Verification Into Your Workflow
Knowing the technical tells of a deepfake is one thing, but actually spotting them on a tight deadline is a completely different ballgame. To consistently fight back against AI-generated media, you need a structured, repeatable process. A random, gut-feeling approach just won't cut it when a story's credibility or a company's security is on the line.
Building a formal workflow for deepfake detection turns media verification from a panicked reaction into a proactive habit. It’s about creating a clear set of steps your team follows every single time suspicious media shows up. This ensures nothing slips through the cracks and minimizes the risk of simple human error.
The whole point is to make verification a natural part of your daily operations, not a frustrating bottleneck that slows everything down.
Creating a Standardized Verification Process
A solid verification workflow isn't just about running a tool. It starts broad with contextual analysis and then zooms in for a detailed technical inspection. The best systems blend good old-fashioned human critical thinking with the speed and precision of AI-powered tools. While every organization’s needs are a bit different, a strong process always has a few core stages.
This simple process flow shows the key steps in a typical deepfake analysis.
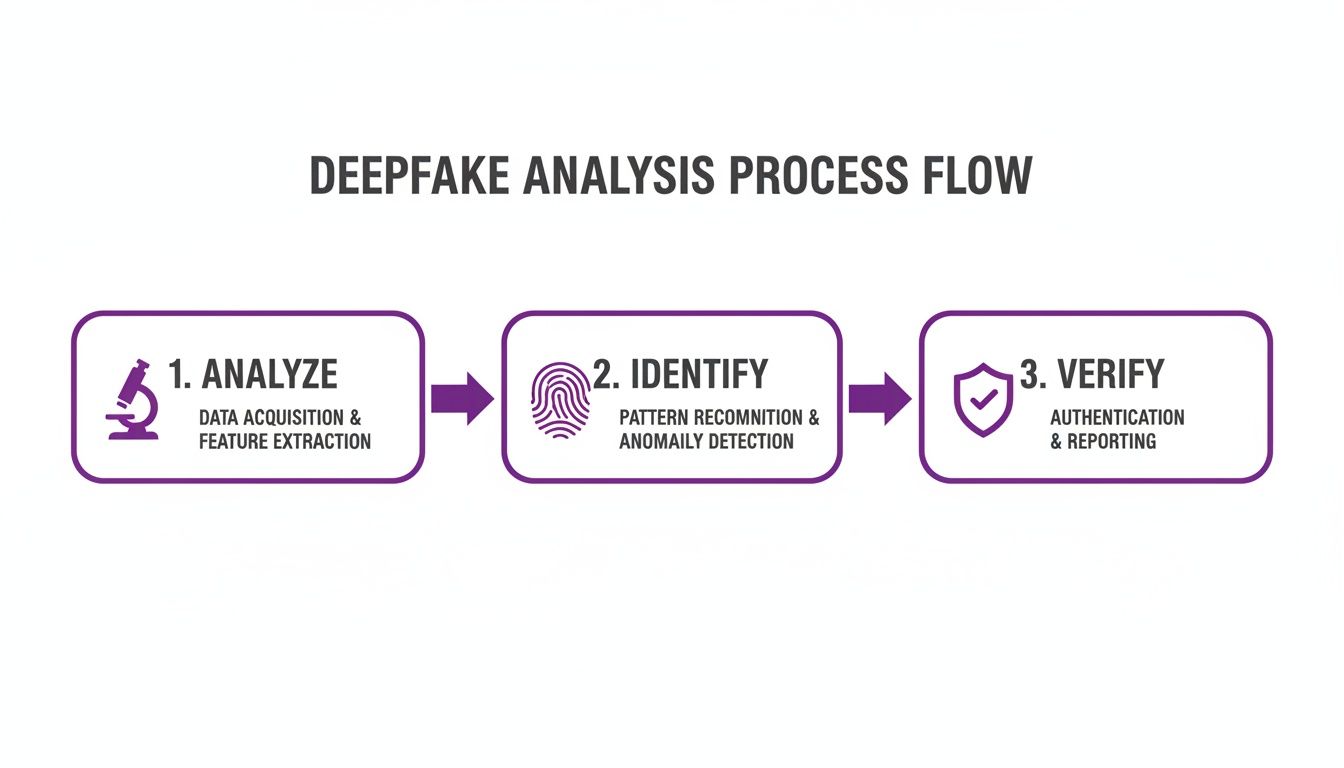
The diagram breaks media verification into three essential phases: a first-pass analysis, a technical identification step, and a final verification. It’s a clear path from initial suspicion to a confident conclusion.
So, what does this actually look like in the real world for different pros?
- For Journalists: The process kicks off with source vetting. Who sent this photo or video? Can you confirm their identity through a separate channel? Next, they check the context. Does the event shown line up with other known facts? Only after those checks do they move to technical analysis, running the file through an AI image detector to scan for digital red flags.
- For Corporate Security Teams: A security workflow might get triggered by an unusual request, like a video message from someone claiming to be an executive who needs an urgent wire transfer. Step one is to hit pause and try to verify the request through a trusted channel—like a direct phone call. At the same time, the suspicious media gets run through a detection tool for an immediate risk assessment.
- For Platform Moderators: Moderators are dealing with a firehose of content, so their workflow has to be lightning-fast. This usually involves an automated first pass, where an API flags potentially fake media. A human moderator then reviews the flagged content, using a detection tool to get a quick second opinion before deciding to take it down or send it up the chain for a closer look.
The most effective workflows don't just lean on technology; they weave it into a larger framework of critical thinking and procedural checks. The tool gives you the data, but the human makes the final, informed call.
Leveraging Tools for Rapid Analysis
In all of these jobs, speed and accuracy are everything. The sheer volume of deepfake attacks has exploded, with some reports showing incidents doubling every month. This surge is driving the demand for verification tools that can give you a reliable confidence score in seconds. A quick look at the latest deepfake statistics shows just how massive this threat has become for organizations.
This is where an AI Image Detector becomes a game-changer. It provides instant, data-driven insights, acting as a force multiplier that allows one person to check media far faster and more accurately than they ever could with just their eyes.
The best tools are designed to be incredibly simple, often featuring a drag-and-drop interface that makes getting a result fast and painless. This design means even non-technical team members can get a clear verdict without a steep learning curve, keeping everyone productive. By embedding a tool like this into your process, you build a system where every piece of outside media can be checked quickly, efficiently, and with a high degree of confidence.
A Closer Look at an AI Image Detector Tool
Knowing the theory behind deepfake detection is one thing, but actually using a tool to spot fakes is where the rubber meets the road. A great AI image detector shouldn't feel like a complicated lab experiment; it should be as intuitive as running a spell-check on a document. The best tools are designed around a few simple ideas that give you clear answers without ever putting your data at risk.
At its core, any detector worth its salt must deliver on three promises: airtight privacy, near-instant speed, and a dead-simple user interface. If a tool fails on any of these, it's just not practical for professionals who need to move quickly.
Privacy isn't a feature; it's a foundation. A tool you can trust will analyze your image without ever saving it to a server. Your files are your business, and they should stay that way.
This is a big deal. It means you can check sensitive news-gathering photos, proprietary business assets, or personal pictures without a second thought. The analysis happens on the fly, and the moment you get your result, the original file is gone. This simple design choice prevents your data from ever being exposed or misused.
How to Use the Tool Step by Step
Getting a verdict on a suspicious image should take seconds, not minutes. The whole point is to move from doubt to clarity without jumping through technical hoops.
- Upload Your Image: It all starts with a simple drag-and-drop. You can either browse for a file on your computer or just pull it right into the analysis window. The tool accepts standard formats like JPEG, PNG, and WebP, with a generous file size limit of up to 10MB for high-resolution media.
- Get the Verdict: Before you can even finish your thought, the analysis is done—usually in under ten seconds. The tool gives you a straightforward, color-coded result that shows you where the image falls on the human-to-AI spectrum.
That speed is everything. A journalist on a tight deadline or a platform moderator sifting through hundreds of posts can't afford to wait. Fast feedback makes rapid verification a reality, fitting neatly into any workflow.
Understanding the Verdict Spectrum
The results from a good AI image detector aren't just a simple "real" or "fake." Life—and AI—is more complicated than that. Instead, you get a result on a spectrum of confidence, which gives you a much more useful and honest assessment.
The verdict will generally land in one of these categories:
- Likely Human: The tool sees all the hallmarks of a genuine photograph and finds no red flags for AI generation. Confidence is very high that it's the real deal.
- Possibly Human: Most signs point to a human creator, but there might be a few oddities. This could be caused by heavy photo editing, strange lighting, or other quirks that muddy the waters a bit.
- Possibly AI-Generated: The detector is picking up on several tell-tale signs associated with AI models. It's not a slam dunk, but there’s enough evidence to be highly suspicious.
- Likely AI-Generated: The image is littered with the digital fingerprints of AI synthesis. The tool is highly confident the image was machine-made.
This spectrum is far more practical than a black-and-white answer. If you want to dive deeper into how these systems work, our guide on the core technology of an image AI detector breaks it down further. By understanding this range, you can make a much sharper judgment call, using the tool’s analysis to inform your decision instead of just taking its word for it.
The Constant Arms Race: Detection vs. Evasion
The effort to spot deepfakes has turned into a high-stakes game of cat and mouse. For every new detection method that researchers develop, AI creators are already figuring out how to sidestep it. This isn’t a theoretical problem—it’s a real, fast-moving technological battle.
Think of it as a digital arms race. On one side, security experts build models trained to find the tiny, almost invisible giveaways of AI manipulation. On the other, deepfake creators use feedback from these very tools to make their fakes even better, training their algorithms to be more convincing and harder to catch.
Adversarial Attacks: The Art of Fooling the Machine
The most sophisticated deepfakes today are born from something called an adversarial attack. These fakes aren't just designed to look real to the human eye; they're specifically engineered to trick the algorithms inside detection tools. It's a bit like a safecracker studying the blueprints of a vault to learn its weaknesses before the break-in.
Deepfake creators can actually test their work against common detection software, tweaking their models over and over until they get a passing grade. Through this process, they essentially train their fakes to become invisible to the very systems built to expose them.
This back-and-forth is accelerating. Some security researchers have found that modern deepfakes can now slip past detection tools over 90% of the time. The financial stakes are massive, with this threat expected to drive $12.5 billion in U.S. fraud losses alone. It’s no surprise, given that voice cloning now requires just a few seconds of audio to create a believable fake. The rise of Deepfake-as-a-Service platforms has put these tools in the hands of anyone, making it easier than ever to craft synthetic identities for scams and social engineering. You can read more about this in a detailed market report on deepfake AI.
Why No Detector is Perfect
Because of this constant evolution, no deepfake detection tool will ever be 100% accurate. The technology simply moves too fast. A detector that works great today could be almost useless in six months against a new generation of AI models.
This isn’t a failing of the technology; it's just the nature of the beast.
- The Novelty Problem: Detectors are trained on deepfakes that already exist. They are fundamentally reactive, which means they're always a step behind and often can't spot a fake made with a brand-new technique they've never seen before.
- The Compression Problem: When you upload a video to social media or send it through a messaging app, the file gets compressed to save bandwidth. This process can accidentally wipe out the subtle digital fingerprints that detection tools need to see, effectively erasing the evidence.
- The "Liar's Dividend": As people become more aware of deepfakes, there’s a new danger. Scammers and politicians can dismiss real, inconvenient videos as fakes, knowing that the public is primed to be skeptical. This erodes trust even further.
The goal of a sophisticated attacker isn't just to bypass a single tool. It's to create a deepfake so flawless that it holds up against a wide range of detection methods, making verification nearly impossible without additional context.
Where the Fight is Headed
Despite the challenges, the defense is getting smarter, too. The future of detection is moving beyond just analyzing pixels and toward more holistic, layered approaches. Two areas show a lot of promise.
- Multimodal Analysis: This means looking at multiple signals at once. Instead of just examining a video, future systems will simultaneously check the audio for signs of cloning, inspect the file’s metadata for tampering, and analyze the context of where and how the media was shared.
- Content Provenance: This is like creating a digital birth certificate for a photo or video. Emerging technologies, like the C2PA standard, embed a secure and verifiable log of a file's history directly into the file itself. You can see what camera took it, when it was taken, and a full history of any edits. This shifts the strategy from trying to spot fakes to proving what’s real.
The arms race is far from over, but the next generation of defenses is focused on giving truth a much better fighting chance.
The Legal and Ethical Minefield of Deepfakes
The technology for spotting deepfakes is impressive, but it’s only half the battle. Once you get past the algorithms and detection models, you step into a dense and complicated maze of legal and ethical questions that we're all just beginning to figure out. As this technology gets easier for anyone to use, it’s forcing some really tough conversations about consent, identity, and what we consider to be "truth."
Think about it: when an AI can perfectly copy someone's voice or superimpose their face onto another video without their permission, what laws have actually been broken? The answer is murky at best. Our legal systems are playing catch-up, trying to apply old rules about impersonation, copyright, and defamation to a completely new kind of problem.
Laws Are Scrambling to Keep Up
Governments around the world are starting to react, but there's no single, unified approach. Some places are passing laws aimed directly at malicious deepfakes, while others are trying to stretch existing statutes to cover situations they were never designed for.
- In the United States: We're seeing a patchwork of state laws emerge. Places like Virginia, Texas, and California have passed laws that make it a crime to create or share deepfakes for specific purposes, like interfering with an election or creating non-consensual pornography.
- In the European Union: The focus is more on transparency. Big regulations like the AI Act and the Digital Services Act are pushing platforms to clearly label AI-generated content. The goal isn't to ban the tech outright, but to make sure people know when they’re looking at something that isn't real.
This piecemeal legal landscape makes one thing crystal clear for any organization: you can't just wait for the law to protect you. You need to get ahead of the problem with your own internal policies.
The real danger of deepfakes isn't just that they can create convincing lies. It's that they give bad actors a way to discredit the truth. When anything could be fake, it becomes easier to dismiss things that are real—a concept known as the "liar's dividend."
Building Your Own Rulebook
If you're a platform moderator, a lawyer, or a compliance officer, this problem is already on your desk. How do you shield your users and your company from harmful deepfakes without stumbling into censorship? It all comes down to creating clear, practical, and enforceable policies.
A solid internal policy needs to spell out exactly what you consider harmful synthetic media and what happens when someone posts it. This usually means drawing a hard line against:
- Non-consensual intimate imagery (revenge porn).
- Content created to bully or harass specific people.
- Media designed to disrupt elections or spread political disinformation.
- Impersonations used for scams or fraud.
Having these rules gives your teams a clear playbook for what to do. It’s not just about risk management; it’s about showing your users you’re committed to their safety, which is essential for building and keeping their trust. When you combine strong internal guidelines with effective deepfake detection tools, you can confidently navigate this thorny new world and help create a safer digital space.
Answering Your Questions About Deepfake Detection
It's natural to have questions when you're dealing with something as complex as synthetic media. Let's tackle some of the most common ones to give you a clearer picture of how deepfake detection works in the real world.
Just How Accurate Are Deepfake Detectors?
This is the big question, isn't it? In a perfect lab environment, the best tools can hit accuracy rates well over 95%. But the internet is anything but a perfect lab.
Out in the wild, where images and videos are compressed, re-uploaded, and shared across platforms, that number changes. A more realistic expectation for a solid, everyday tool is somewhere in the 65-85% range. That's why no detector should be your only source of truth; it's a powerful signal, but it has to be part of a bigger verification process that includes good old-fashioned critical thinking.
Can a Detector Ever Be 100% Sure Something Is Fake?
Nope. Be very skeptical of any service that promises 100% certainty. Think of it as a constant cat-and-mouse game: as the detectors get smarter, so do the AI models pumping out the fakes.
This is why the best tools don't just give you a simple "real" or "fake" answer.
A trustworthy detector will give you a confidence score, something along a spectrum from "Likely Human" to "Likely AI-Generated." This approach is more honest about the technology's limits and gives you the context you need to make a judgment call.
What’s the First Thing I Should Do If a Tool Flags Content as a Deepfake?
If you get a positive hit from a detector, the most important first step is to simply pause. Don't share it, don't react, don't do anything else until you've investigated. Treat the flag as a strong prompt to dig deeper.
- Hunt for the source: Where did this image or video originally come from? A well-known news agency or a random, anonymous account? The origin story matters.
- Look for backup: Are other credible sources talking about this? If no one else is reporting it, that's a huge red flag.
- Use your gut: Does the content even make sense? Is it designed to make you angry or scared? Emotional manipulation is a classic sign of mis- and disinformation.
Are Some Fakes Trickier to Catch Than Others?
Yes, without a doubt. The easiest fakes to create are often the easiest to spot. The real challenge comes from subtle edits.
Things like minor tweaks to facial expressions or syncing lips to new audio—without swapping the whole face—can slip past many detectors. High-quality audio deepfakes are also a massive headache, often requiring specialized forensic tools to catch tiny, synthetic artifacts in voice patterns. As the generation tools get more sophisticated, these subtle fakes will only become a bigger problem.
Ready to add a powerful layer of verification to your workflow? AI Image Detector offers fast, private, and reliable analysis to help you spot AI-generated fakes in seconds. Try it for free and make smarter, safer decisions.


