The Ultimate Guide to a Deepfake Image Maker
So, what exactly is a deepfake image maker? In simple terms, it's an AI-powered tool designed to create incredibly realistic—but completely fake—images and videos. The classic example is digitally placing one person's face onto someone else's body, but the technology has grown far more sophisticated than that.
What Is a Deepfake Image Maker and Why Should You Care?

At its heart, a deepfake image maker relies on a type of artificial intelligence called deep learning to produce what’s known as synthetic media. The AI system is fed a huge dataset—hundreds or thousands of photos and videos of a person—to meticulously study their facial expressions, movements, and even their voice. Once it "learns" that person, it can generate entirely new content, making them appear to do or say things they never did.
This isn't sci-fi anymore. The technology has escaped the confines of research labs and Hollywood studios. Thanks to a boom in easy-to-use apps and accessible AI models, these powerful creation tools are now available to anyone with an internet connection. What started as a niche experiment has quickly become a mainstream problem, forcing us all to confront difficult questions about truth and digital identity.
The Alarming Rise of Deepfake Misuse
With this newfound accessibility comes a dark side: a dramatic spike in malicious use. The data paints a stark picture of how quickly this problem is spiraling out of control.
According to a Surfshark report, deepfake incidents are exploding. The numbers show a clear and worrying trend:
- The first quarter of this year alone saw 179 reported incidents—a 19% increase over the entire previous year.
- The prior year had 150 incidents, which was already a shocking 257% jump from the year before that.
- The most common misuse was creating explicit content, with 53 reported incidents, more than doubling from 26 the year prior.
This isn't just a problem for celebrities and politicians, either. The report found that 56% of cases targeted private, everyday individuals. The ease of creating this content has turned it into a weapon for misinformation, harassment, and fraud on a massive scale.
Deepfake Threat Landscape at a Glance
The proliferation of deepfake image makers creates a complex web of threats that touch nearly every aspect of our digital lives. From personal security to global politics, the potential for harm is significant. The table below outlines the primary areas where these threats are most acute and who is most affected.
| Affected Area | Primary Threat | Key Audience |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Security | Non-consensual explicit content, identity theft, personal harassment, and blackmail. | Private citizens, particularly women and vulnerable individuals. |
| Corporate & Brand Reputation | Fake executive statements, fraudulent endorsements, brand sabotage, and stock market manipulation. | Businesses, executives, and public relations teams. |
| Journalism & Media | Disinformation campaigns, erosion of public trust in media, and fabricated "evidence" in news stories. | Journalists, fact-checkers, news organizations, and the general public. |
| Politics & Elections | Misleading campaign materials, fake candidate videos, voter suppression, and geopolitical destabilization. | Politicians, government agencies, voters, and election officials. |
As you can see, the ripple effects are far-reaching. What starts as a single fake image can undermine trust across entire industries and institutions.
Why This Matters to You
Understanding what a deepfake image maker is and how it works has become a fundamental digital literacy skill. The line between what's real and what's fake has never been so blurry, and that has serious consequences for all of us.
The core issue isn't just that fake content exists; it's that it can be created and distributed at an unprecedented scale, undermining trust in everything we see online.
Whether you're a journalist trying to verify a source, a business owner protecting your brand, or just a regular person scrolling through social media, you need to know how to spot the fakes. This guide is designed to give you the practical knowledge and tools to do exactly that.
How a Deepfake Image Maker Actually Works
You don't need a computer science degree to get the gist of how a deepfake image maker works. The best way to think about it is as a creative duel between two AIs: a Master Artist and a Sharp-Eyed Critic.
The Master Artist’s only job is to paint fakes. It just keeps churning out new images, doing everything it can to fool the Critic. The Critic, on the other hand, has one mission: spot the forgeries. It looks at every single image and gives it a thumbs-up ("real") or a thumbs-down ("fake").
This constant tug-of-war is the secret sauce.
Every time the Critic catches a fake, the Artist learns from the feedback. It tweaks its technique, gets a little smarter, and tries again. This back-and-forth happens thousands, sometimes millions, of times.
This competitive setup has a technical name: a Generative Adversarial Network, or GAN. The ongoing battle between the generator (the Artist) and the discriminator (the Critic) is what pushes the generator to create fakes that get better and better, eventually becoming almost impossible to distinguish from the real thing.
Eventually, the Artist gets so good that the Critic can barely tell the difference anymore. At that point, you have a synthetic image that can easily fool a person.
The Core Generation Process
While the software might look different from one tool to the next, the underlying process for creating a deepfake is pretty much the same everywhere. It boils down to three main stages that build on each other to produce the final image.
Data Collection: First, you need raw materials. The AI needs a ton of pictures and videos of both the "source" person (whose face you're using) and the "target" (the image or video you're putting the face onto). We're talking hundreds or even thousands of high-quality examples showing different angles, lighting, and expressions. The more data you feed it, the better the AI gets at learning someone’s unique facial tics and features.
Model Training: This is the learning phase. All that collected data is fed into the AI model. Using a process called deep learning, the system analyzes and maps out the facial structures of both the source and the target. It pinpoints key landmarks—the shape of the eyes, the curve of the mouth, the line of the nose—and learns how they move together. To really get a handle on how these models work, it helps to know about the neural networks that power them. For example, understanding the basics of Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) sheds light on how AI can process sequential information, like the frames in a video.
Image Generation: With the training complete, it's time to create the deepfake. The AI painstakingly swaps the source face onto the target's body, going frame by frame. It has to adjust for lighting, head orientation, and expressions to make the blend look natural. Finally, the system renders the output: a brand-new, synthetic image or video that looks convincingly real.
Visualizing the GAN Framework
The diagram below gives you a clear picture of this adversarial process between the Generator and the Discriminator, which is the engine inside a GAN.
As you can see, the Generator takes random noise and tries to turn it into a believable sample. The Discriminator's job is to tell that fake sample apart from real data. This feedback loop forces the system to learn and improve at an incredible rate, making it a powerful tool for any deepfake image maker.
Understanding the Real-World Risks of Deepfakes

While the technology powering a deepfake image maker is undeniably clever, its potential for harm is both profound and alarmingly widespread. These aren't abstract, futuristic problems; they're happening right now, affecting real people, businesses, and even global stability. To build any meaningful defense, we first have to grasp the threats we're up against.
Think about it. A journalist gets a video appearing to show a political candidate taking a bribe just days before an election. A CFO receives a voice-cloned call from their CEO, urgently demanding a massive wire transfer to an unfamiliar account. These scenarios have jumped from spy movies to our daily reality.
The malicious use of deepfakes runs the gamut, from political misinformation campaigns to deeply personal attacks and sophisticated financial scams. Grounding these threats in real-world examples makes it clear why robust detection tools are no longer a luxury—they're a necessity for everyone.
The Spectrum of Malicious Use
Malicious deepfakes are used in countless ways, but they tend to fall into a few key categories, each with its own destructive potential. This is how a single piece of synthetic media can ripple out and cause immense damage.
- Political Disinformation: Fabricated videos can invent scandals, push false narratives, or stoke social unrest, directly undermining democratic processes.
- Corporate Sabotage: Imagine a fake audio clip of a CEO announcing terrible quarterly results. It could crash a company's stock price or shatter its reputation in minutes.
- Financial Fraud: Voice cloning and video deepfakes are used to impersonate people to authorize fraudulent payments or breach sensitive accounts.
- Personal Harassment: This is arguably the most common and devastating use. It targets individuals with non-consensual explicit content for blackmail, revenge, or pure cruelty.
Personal Devastation and Identity Theft
For an individual, the impact of a malicious deepfake can be absolutely life-altering. The creation of non-consensual explicit material is a particularly vicious form of abuse. Anyone can scrape a person’s public photos from social media and feed them into an AI to create realistic—and fake—explicit images or videos, causing severe emotional trauma and reputational ruin.
This isn't just a hypothetical. Victims have shared horror stories of finding AI models of themselves being passed around online, allowing strangers to generate an endless stream of fake, explicit images. The sheer ease of use means this kind of harassment can be scaled at a rate we've never seen before, leaving victims feeling helpless.
A single photo is often all a deepfake image maker needs to start generating fraudulent content. This material is then used for everything from bullying and blackmail to "sextortion" schemes, which have become one of the fastest-growing cybercrimes targeting young people.
This erosion of trust extends to outright identity theft. Scammers can use deepfaked videos to fool biometric security checks on banking apps or create fake social media profiles to trick friends and family into wiring them money. The very idea of visual proof is under attack.
Corporate and Financial Fraud on a Grand Scale
The business world is grappling with a new and unprecedented wave of fraud fueled by deepfake technology. The numbers are staggering and paint a grim picture of the financial risk.
Deepfake files shared online skyrocketed from 500,000 to a projected 8 million in just two years. That’s a nearly 900% annual growth rate, turning this threat into a viral epidemic. The cryptocurrency sector alone absorbed 88% of deepfake fraud in a recent year (a tenfold increase from the previous year). Overall, this type of fraud now makes up 6.5% of all attacks, with a stunning 2,137% growth rate. Financial professionals have seen a 53% jump in scam attempts, while older Americans lost $3.4 billion to fraud—an 11% increase year-over-year. You can learn more about the escalating deepfake threat and its financial impact from this detailed analysis.
This surge is largely driven by sophisticated scams like Business Email Compromise (BEC), where attackers use cloned voices to authorize payments. In one infamous case, a UK energy firm was tricked into sending $243,000 after an employee received a call from a perfect voice deepfake of his boss. The growing accessibility of deepfake tools means these attacks are only getting cheaper and more common, putting businesses of every size in the crosshairs.
How to Spot a Deepfake With Your Eyes and With AI
Now that we understand the risks, the big question is: what can we do about it? How do you tell a real image from something cooked up by a deepfake image maker? The best defense is a combination of old-school human observation and new-school technology.
Your own eyes are always the first line of defense. Many of the less sophisticated deepfakes still have little glitches and giveaways that you can catch if you know what to look for. Think of it as developing a digital intuition.
But let's be realistic—the technology is getting scarily good. The most advanced fakes are so polished they can fool almost anyone. They leave behind tiny, invisible traces that our eyes and brains simply can't process. That's where AI detection tools become non-negotiable, adding a crucial layer of forensic analysis.
Visual Red Flags You Can Look For
Before you run an image through a tool, always give it a quick once-over yourself. This manual check can often weed out the low-effort fakes. The trick is to stop looking at the big picture and start focusing on the tiny details where the forgery falls apart.
Here are a few common giveaways to keep an eye out for:
- Unnatural Facial Movements: People in deepfakes often have weird blinking patterns—blinking way too often or not at all. A smile might not reach the eyes, making it look forced, or their whole expression can feel stiff and robotic.
- Awkward Head and Body Positioning: Does the person's head sit weirdly on their neck? Look closely at the edges where the face meets the hair or jawline. You'll often find blurry spots, mismatched skin tones, or smudged lines.
- Inconsistent Lighting and Shadows: This is a classic mistake. The light on the person's face might be coming from the left, but the shadows in the background suggest the light source is somewhere else entirely. It just feels... off.
- Digital Artifacts and Glitches: Don't be afraid to zoom in. Look for weird pixelation, skin that looks too smooth like a wax figure, or reflections in the eyes that don't match the environment they're supposed to be in.
A critical tell is often in the details that AI struggles to replicate perfectly, like the fine strands of hair, the natural texture of skin pores, or the way light reflects off of teeth and eyes. These are the elements that can betray a synthetic origin upon close inspection.
For a deeper dive into spotting these subtle cues, our guide on how to spot a deepfake offers more detailed examples and techniques.
Why the Human Eye Is No Longer Enough
While these manual checks are a great starting point, they have a major weakness: us. We're only human. As deepfake image maker tools get more powerful, they're creating fakes that are virtually indistinguishable from reality, at least to our eyes. Those little errors we used to rely on are vanishing fast.
The numbers here are pretty sobering. On average, people can correctly identify deepfake images only 62% of the time. When it comes to video, that accuracy craters to a shocking 24.5%. This gap shows why just "using your best judgment" is a risky game, especially with so much on the line. Deepfake scams exploded by 3,000% in just one year, and malicious deepfake attempts are up by that same jaw-dropping figure. You can dig into the specifics of this threat in these deepfake and AI phishing statistics.
Human vs AI Detection Capabilities
When it comes to telling real from fake, both the human eye and AI detectors bring something different to the table. Here’s a quick breakdown of where each one shines—and where they fall short.
| Detection Method | Strengths | Weaknesses | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human Eye | Can quickly spot obvious, low-quality fakes. Good at sensing "uncanny valley" weirdness and contextual issues. | Easily fooled by high-quality fakes. Prone to biases and fatigue. Accuracy drops significantly with video. | A quick, initial gut-check for obvious forgeries. |
| AI Detector | Analyzes images at a pixel level, finding invisible artifacts. Detects subtle patterns left by generative models. Fast, scalable, and objective. | Can sometimes produce false positives/negatives. Requires continuous updates to keep up with new generative models. | Forensic-level verification, analyzing high-quality fakes, and processing images at scale. |
Ultimately, while our eyes provide a valuable first pass, an AI tool offers the kind of deep, forensic analysis that's necessary to keep up with modern deepfakes.
The Power of AI-Powered Detection
This is exactly where specialized AI detection tools come in. They aren't looking for a weird smile or bad lighting. Instead, they dig into the very fabric of the image, analyzing it on a mathematical level to find the digital DNA left behind by the AI that created it.
An AI detector doesn't see a "face"—it sees a massive grid of pixels, color data, and compression artifacts. It has been trained on millions of real and AI-generated images, teaching it to recognize the invisible signatures that separate the authentic from the synthetic. This includes looking for things like:
- Pixel-Level Inconsistencies: It can spot microscopic noise patterns and artifacts that are unique to certain AI generation models.
- Frequency Analysis: The tool can analyze an image’s frequency domains to find patterns that don't match how a real camera sensor works.
- Geometric Irregularities: It can detect tiny inconsistencies in facial symmetry or 3D mapping that are completely invisible to us.
These same core principles are being applied across industries, with methods like machine learning fraud detection showing how technology can be a powerful ally against deception. At the end of the day, an AI detector gives you the speed, scale, and accuracy that our eyes just can't deliver, making it an essential part of any modern verification process.
Your Practical Workflow for Verifying Digital Media
Knowing the red flags of a deepfake is one thing, but turning that knowledge into a reliable, repeatable process is another challenge entirely. For professionals like journalists, researchers, and content moderators, having a structured workflow is non-negotiable for making fast, confident decisions.
Let's break down a hands-on verification process into four actionable steps you can start using today.
This simple decision guide shows how to move from a quick visual check to a more detailed scan when you're on the fence.
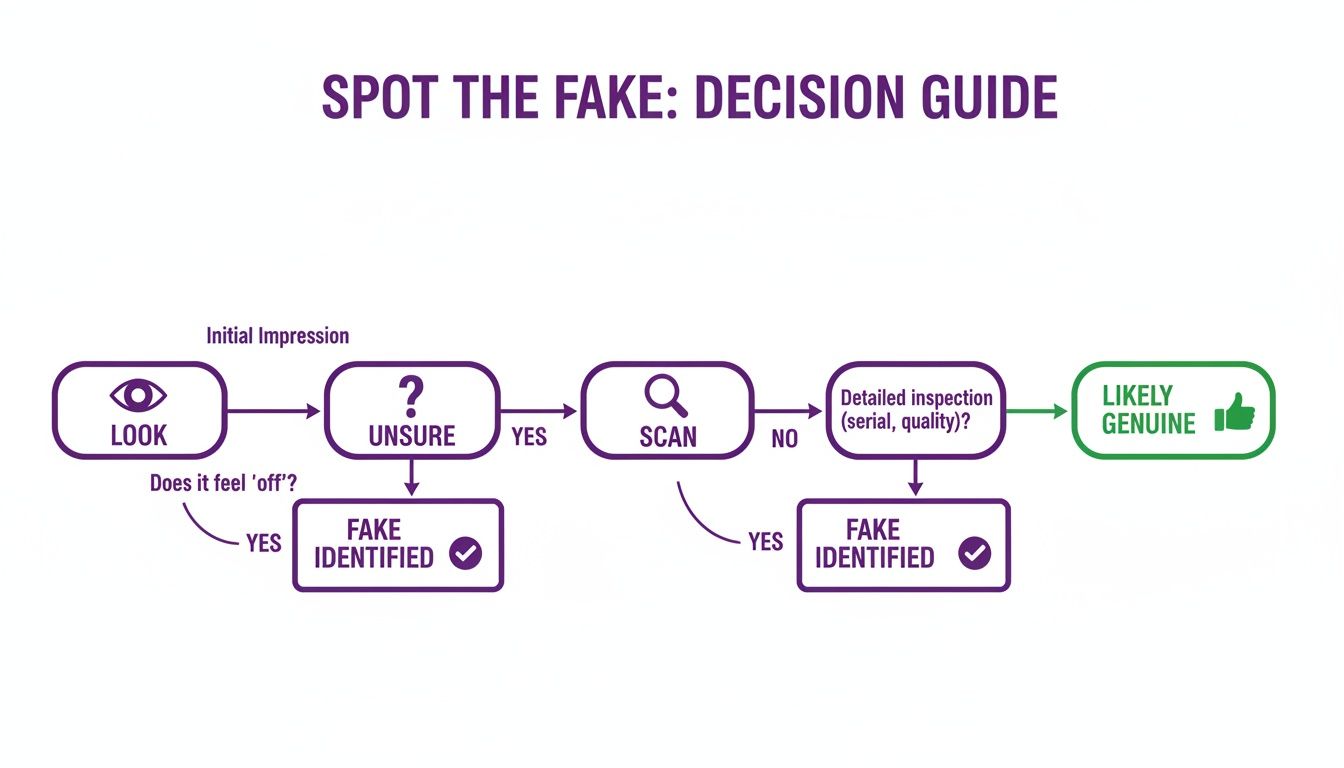
The key is to trust your initial instincts but always fall back on deeper analysis whenever a shred of doubt remains.
Step 1: Start with a Human Review
Your first pass should always be a quick, manual inspection. Before you even think about using a tool, take 30 seconds to look for the obvious giveaways we've already covered. This initial check is all about catching the low-hanging fruit—the less sophisticated fakes you can dismiss right away.
Ask yourself these simple questions:
- Do the eyes look right? Are there strange blinking patterns or unnatural reflections?
- Is the lighting consistent? Do the shadows on a person match the background they're in?
- Are there blurry or weird edges? Pay close attention to the hairline and jawline for signs of sloppy digital blending.
This gut-check phase is surprisingly effective at weeding out amateur forgeries. But if anything feels even slightly off, or if the image looks a little too perfect, it’s time to dig deeper.
Step 2: Use an AI Image Detector
When your eyes can't give you a clear answer, an AI detection tool becomes your most powerful ally. Submitting an image to a service like AI Image Detector is as easy as it gets—just drag and drop the file, and the platform gets to work.
Behind the scenes, the tool isn't just "looking" at the picture. It's running a deep forensic analysis, scanning for pixel-level artifacts, frequency domain irregularities, and other invisible signatures left behind by a deepfake image maker. These are the digital fingerprints that even the most advanced fakes struggle to hide completely.
This isn't about opinion; it's about data. The AI detector compares the image’s underlying mathematical structure to a massive database of both real and AI-generated content, hunting for statistical patterns that betray its synthetic origin.
Step 3: Interpret the AI Report
In seconds, the detector will give you a report. This usually includes a confidence score and a clear verdict, like "Likely Human" or "Likely AI-Generated." Knowing how to read this report is crucial.
A high confidence score (say, 95% Likely AI-Generated) is a pretty strong indicator that you’re looking at a fake. A low score might mean the image is authentic, or perhaps that it’s only been subtly edited. Some tools even provide heatmaps that highlight specific areas of manipulation, which adds a ton of context.
Beyond what you see, valuable information is often hidden within the file itself. For a more technical angle, you can learn how to check metadata of photo files to find clues about their origin and edit history.
Step 4: Decide on Your Next Steps
The final step is to act on the information you've gathered. What you do next depends entirely on your role and the context of the image.
Here’s a simple framework to follow:
- High Confidence of AI Generation: If the tool is confident it's a fake, the path forward is clear. For a journalist, that means killing the story. For a moderator, it means removing the content and maybe flagging the user account.
- High Confidence of Human Origin: If the report says the image is likely real, you can proceed with much more confidence. Still, always consider the source and context as part of your overall verification process.
- Ambiguous or Mixed Results: If the results are inconclusive, you have to exercise extreme caution. This could mean it's a real photo that has been heavily edited. In these situations, the safest bet is to treat the image as unverified and look for more corroborating evidence.
Navigating the Legal and Ethical Maze of Deepfakes
Knowing how to spot a synthetic image is a crucial skill, but it's really just the first step. The explosion of deepfake image maker tools has thrown us into a complex and often murky world of legal and ethical questions. For professionals in almost any field, getting a handle on these challenges isn't just a good idea anymore—it's a core part of doing your job responsibly.
At the heart of it all are two simple words: consent and intent. What one person might create as a harmless meme, another can experience as a deeply personal attack on their identity and privacy. It's in this gray area that new laws and professional ethics are being forged, demanding a much higher standard from anyone who creates, shares, or reports on digital content.
Guidance for Journalists and Media Professionals
If you're a journalist, the ethical tightrope is particularly precarious. Your first duty is to the truth, and running a story with unverified or fake media can shatter the public's trust in an instant. Before any image or video makes it into a report, it has to go through a serious, multi-layered verification process.
This isn't just about catching errors. It's about actively fighting the tide of disinformation. When a news outlet publishes a deepfake, even by accident, it gives the fake a stamp of legitimacy that's incredibly hard to take back. The ethical guideline has to be crystal clear: verify first, publish later. Anything less is a failure of journalistic integrity.
The sheer ease with which a deepfake image maker can create believable fakes means we can no longer take visual "evidence" at face value. A documented, step-by-step verification workflow is now an absolute must-have for ethical reporting.
Legal Risks for Corporations and Platforms
For a company's legal team or a platform's moderation staff, the game is all about managing risk. Deepfake technology is already being used for everything from financial fraud and targeted harassment to sabotaging a brand's reputation. More and more, companies are expected to have systems in place to get ahead of these problems. Having a documented verification process isn't just a "best practice"—it's a crucial line of defense if you end up in court.
New regulations are also starting to hold companies and platforms responsible for the harmful fakes spreading on their watch. For example, laws like Connecticut's Public Act 23-168 now make it a crime to share non-consensual deepfakes of an intimate nature. A company that ignores reports of this kind of content on its platform could find itself facing major legal and financial blowback.
Protections for Creators and Individuals
For artists, photographers, and other creators, the biggest worry is seeing their work and their own faces used without permission. AI models are frequently trained on massive datasets of images scraped from across the internet, often without the creator's knowledge or consent. This raises huge questions about copyright and who really owns what online.
Creators are starting to push back, fighting to stop their art and identities from being fed into a deepfake image maker. The legal system is still playing catch-up, but the ethical argument is simple: a person's likeness and their creative output shouldn't be used to train an AI without their express permission. How this battle plays out will likely shape the future of digital ownership for years to come.
Got Questions About Deepfake Image Makers? We've Got Answers.
As this technology becomes more common, it’s completely normal to have questions. Let's break down some of the most common things people wonder about when it comes to deepfakes.
Can a Deepfake Be 100% Undetectable?
In theory, no. In practice, it’s getting incredibly difficult to tell. Every AI model leaves behind microscopic, invisible artifacts—think of it as a faint digital fingerprint. So while a deepfake image maker can easily create something that fools the human eye, sophisticated detection tools can often pick up on these tiny mathematical traces.
The catch is, as the AI gets better, those fingerprints get fainter and harder to find. It’s a constant cat-and-mouse game between the people making fakes and the people building tools to detect them. For now, a well-made deepfake will fly right past the average person without a second glance.
What's the Difference Between a Deepfake and a Photo Edit?
The real difference is how they’re made. A classic photo edit is done by a person using a tool like Photoshop. They are manually changing the original image—maybe removing a background object, changing colors, or pasting one person’s head onto another body. It's a direct manipulation of the pixels that were already there.
A deepfake is something else entirely. It's generated by an AI model that has learned what a person looks like from a set of training photos. The AI then creates brand-new pixels from scratch to build a new image or video. It’s an act of pure digital creation, not just alteration.
Think of it like this: photo editing is cutting up magazines to make a collage. Creating a deepfake is teaching a robot to paint a brand-new portrait of someone from memory.
How Can I Protect My Photos from Being Used in a Deepfake?
Protecting your images in the age of AI is tough, but you can take a few important steps. First, lock down the privacy settings on your social media accounts. This makes it harder for strangers to access and download your photos.
It’s also smart to just be more cautious about what you post publicly. For some of the latest deepfake tools, all it takes is one clear, high-quality photo of your face to get started.
What's Next for Deepfake Technology?
The future is all about more realism and easier access. We're heading toward real-time video deepfakes that are completely seamless, along with AI that can create a convincing fake from just a tiny bit of source material, like a single photo or a short audio clip.
This shift means that AI-powered detection tools won't just be helpful—they'll be an essential line of defense for anyone who needs to confirm what’s real and what isn’t.
Don't get caught by a fake. AI Image Detector offers fast, free, and accurate analysis to tell you if an image is human or AI-generated. Verify your images with confidence today.



