How Photo Recognition Software Actually Works
Ever wonder how your smartphone can find every picture of your dog just by searching for "dog"? Or how social media platforms instantly suggest tags for your friends in photos? That's photo recognition software at work. It’s a form of AI that doesn't just see pixels; it learns to interpret what those pixels represent—be it a face, an object, or an entire scene.
Unlocking the Power of Digital Sight
At its heart, photo recognition software acts as a translator for the visual world. It takes the raw, messy data of an image—millions of colored dots—and pulls out meaningful information. Instead of a jumble of light and shadow, the software sees patterns and can confidently label what's in the picture. Think of it like your own brain, which can spot a friend in a crowded room instantly without having to consciously analyze their every feature.
This technology has quietly woven itself into our daily routines. When you search your photo gallery for "beach" and seconds later see all your vacation snaps, you're interacting with it directly. It’s the invisible assistant organizing your digital memories so you don’t have to.
The Foundation of Modern Visual AI
This isn't magic; it's the result of combining computer vision with machine learning. To get there, a system is fed a massive training library—we're talking millions of images that have already been labeled by humans. By studying this data, the AI learns to connect specific pixel patterns with things in the real world.
- Object Identification: It learns the difference between a car and a bicycle, or a cat and a dog.
- Facial Recognition: It can pinpoint unique facial structures to distinguish one person from another.
- Scene Understanding: It moves beyond just objects to grasp the bigger picture, like identifying a "birthday party" or a "soccer game" based on all the elements present.
To give you a better grasp of these concepts, here’s a quick overview.
Photo Recognition At A Glance
This table breaks down the fundamental aspects of photo recognition software, from its core function to the technologies that make it possible.
| Concept | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Core Function | To analyze the pixel data in an image and assign meaningful labels to its contents. | Identifying a "golden retriever" in a photo. |
| Key Technology | Computer Vision and Machine Learning models trained on vast, labeled image datasets. | An algorithm trained on 1 million cat images. |
| Real-World Use | Automating tasks that require visual interpretation, from photo organization to security systems. | Unlocking your phone with your face. |
This technology is branching out in some seriously creative directions. We’re now seeing powerful interior design software 3D rendering that lets you snap a picture of a room and instantly see how new furniture would look in it. For a deeper dive into the mechanics, our guide on how image recognition software works is a great next step.
Photo recognition isn't just about organizing your vacation pictures anymore. It's about turning images into searchable, intelligent data that can boost efficiency and open doors to new ideas in almost any field.
The financial numbers back this up. The global image recognition market is booming, projected to hit around USD 71.41 billion by 2026. That’s a huge leap from its USD 53.3 billion valuation in 2023, which shows just how deeply this technology is embedding itself into the global economy. You can find more details about the image recognition market on Towards ICT.
Teaching a Computer How to See
How exactly does a machine learn to look at a chaotic grid of pixels and confidently say, "That's a cat"? It’s a process that feels incredibly complex, but the core idea is more intuitive than you might think. It all starts by translating what we see into a language a computer understands: numbers.
Every digital photo you’ve ever taken is, at its heart, just a massive grid of pixels. Each one of those tiny dots has a numerical value assigned to it, representing its specific color and brightness. To a computer, your prize-winning photo of a golden retriever isn't a furry friend; it’s a sprawling array of millions of data points. The real magic of photo recognition software is its ability to find meaningful patterns in that numerical chaos.
From Digital Flashcards to Feature Detection
Think about how you’d teach a toddler to identify animals. You'd probably use flashcards, showing them hundreds of pictures while repeating "cat," "dog," or "bird." Over time, that child starts to pick up on the common features—pointy ears and whiskers usually mean "cat," while a wagging tail and a wet nose probably point to "dog."
Training a machine learning model is surprisingly similar. Developers feed it a colossal dataset with millions of images that have already been labeled by humans. The model sifts through all this data, slowly learning to connect specific numerical patterns with the right labels.
At first, it starts with the absolute basics, learning to spot simple features. These are the fundamental building blocks of any image:
- Edges: The lines where one object stops and another one starts.
- Corners: The points where different edges meet.
- Textures: Repeating patterns you'd recognize, like fur, grass, or wood grain.
- Colors: Patches of similar shades and tones.
From there, the model starts piecing these simple features together to form more complex shapes. It learns that certain lines and curves make up an eye, and that combining eyes with a nose and a mouth creates a face. This hierarchical process—building up from simple lines to intricate objects—is the cornerstone of modern computer vision.
Distinguishing Between Objects, Scenes, and Faces
Once a model gets good at identifying these basic shapes and structures, it can be fine-tuned for more specific jobs. The underlying technology is similar, but how it's applied changes a lot depending on the goal.
This simple workflow gives you a high-level look at how an image gets processed, moving from raw input to an intelligent, tagged output.
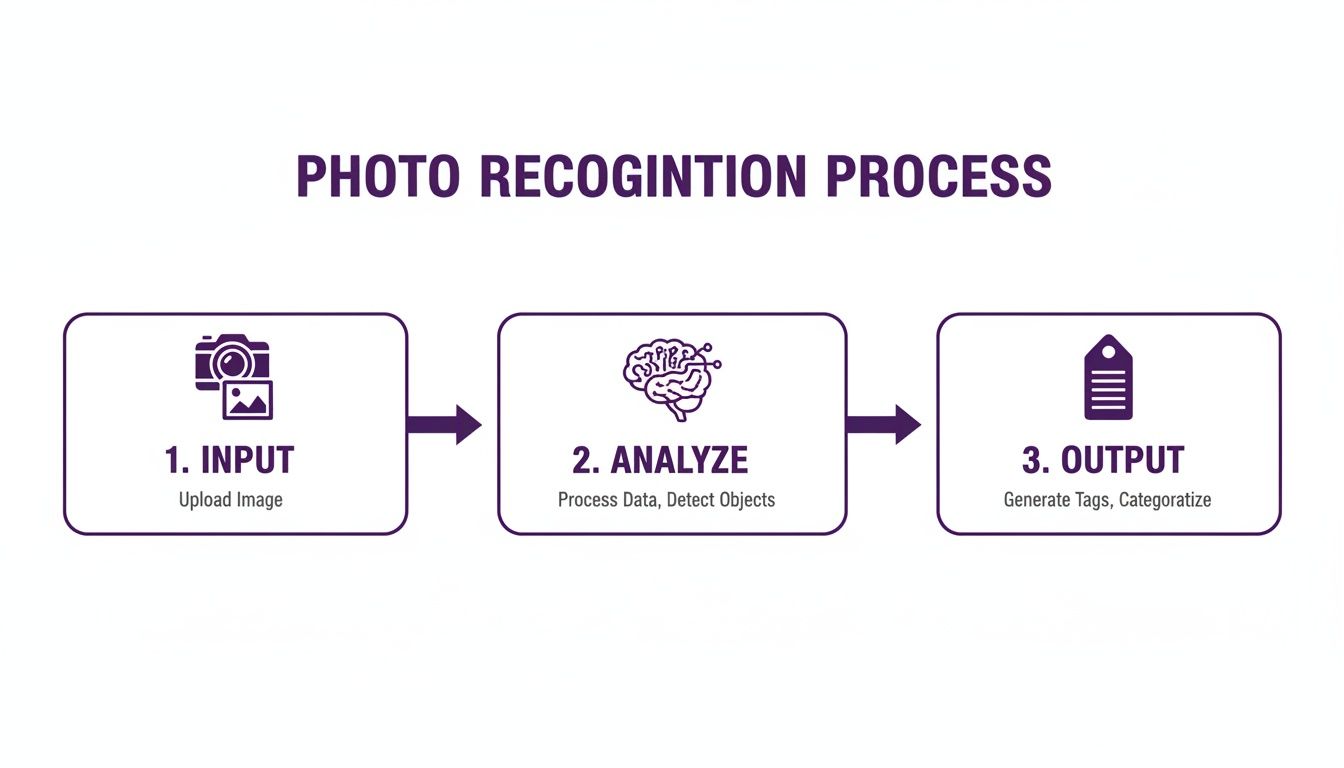
As the diagram shows, recognition isn't a single event. It’s a structured, analytical process that transforms raw visual data into genuinely useful information.
There are three main categories of recognition that build on this foundation:
Object Detection: This is all about finding and identifying specific items within a picture. It’s built to answer two key questions: "What is in this image?" and "Where is it?" Think of an e-commerce app that lets you search with your camera—it uses object detection to spot the handbag in your photo and draw a little box around it.
Scene Recognition: This takes a much broader, more holistic view. Instead of just picking out a "cake," "balloons," and "people," scene recognition software pieces together the context and labels the entire image as a "birthday party." It’s designed to interpret how all the different objects relate to one another to understand the bigger picture.
Facial Recognition: This is a highly specialized form of object detection that focuses only on human faces. It does more than just find a face; it analyzes unique biometric features—like the distance between the eyes, the shape of the nose, and the contour of the jawline—to create a unique digital signature. This "faceprint" can then be used to verify someone's identity with incredible accuracy, sometimes exceeding 99% in controlled environments.
No matter the application, the core principle is always the same: find the patterns. Whether it's the pattern of a bicycle's wheels, the collection of patterns that define a beach scene, or the unique biometric pattern of a human face, the software is trained to connect visual data to a real-world concept.
A really interesting application of this is Generative AI Inpainting, where an AI intelligently fills in missing or removed parts of an image. This requires a deep contextual understanding, as the software has to "see" what should be there based on all the surrounding pixels.
If you want to dig deeper into the tools behind this, our article on the AI image analyzer goes into much more detail. By breaking images down into data it can understand, a computer can now perform visual tasks that, not long ago, we thought were exclusively human.
Photo Recognition in The Real World

The theory behind photo recognition is one thing, but its real magic happens when it's put to work solving actual problems. Across dozens of industries, this technology is already creating new opportunities and fundamentally changing how things get done, from how we shop to how doctors diagnose disease.
Ever seen someone wearing the perfect pair of shoes but had no idea what they were? Instead of fumbling with descriptive search terms, you can just snap a picture. E-commerce apps with a visual search feature let you upload that photo, and within moments, the photo recognition software identifies the exact product and gives you a link to buy it. It’s a simple but powerful idea that turns the entire world into a shoppable catalog.
Enhancing Safety and Security
Beyond shopping, photo recognition is a serious player in making our environments safer. Old-school security systems depended on a human watching a bank of monitors, but today's systems are supercharged with AI that can see and think. They analyze live video feeds to automatically spot and flag things that are out of the ordinary.
Think about a restricted area in an office building. Instead of a guard having to keep eyes on everything at once, the software can:
- Spot Unauthorized Access: The system knows who belongs. If an unfamiliar face shows up in a secure zone, it can send an immediate alert.
- Flag Suspicious Objects: It can be trained to recognize when an object, like a backpack, is left unattended for too long in a busy airport, helping head off potential threats.
This kind of automated vigilance helps security teams respond faster and smarter, putting their focus where it’s needed most. Law enforcement uses similar technology to scan public footage for missing persons or identify suspects, cutting down investigation time by matching faces against official databases.
Revolutionizing Medical Imaging
Nowhere are the stakes higher than in healthcare, where quickly and accurately interpreting a medical image can save a life. Radiologists train for years to spot the tiniest anomalies in X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. Photo recognition software has become their new, incredibly powerful assistant.
AI models are fed enormous datasets of medical scans, teaching them to pick up on subtle patterns that might signal diseases like cancer or diabetic retinopathy. These tools aren't here to replace doctors; they act as a second set of tireless, perfectly trained eyes. The software can highlight areas of concern that a human expert might overlook due to fatigue after a long shift.
For example, an algorithm might detect cancerous nodules in a lung scan at a much earlier stage than would otherwise be possible, which can completely change a patient's prognosis. It’s a clear case of technology amplifying human expertise to produce better, faster diagnoses.
By processing visual data with superhuman speed and accuracy, photo recognition technology helps medical professionals make more informed decisions, ultimately saving lives. It turns a static image into a source of deep, actionable insight.
Powering Autonomous Navigation
Maybe the most visible example of photo recognition at work is in the automotive world, where it acts as the "eyes" for self-driving cars. For a vehicle to navigate a busy street safely, it has to constantly see and understand what’s happening around it in stunning detail.
A self-driving car’s cameras are always rolling, feeding a torrent of images to its onboard computer. The photo recognition software is working in real-time to:
- Detect and Classify Objects: It tells the difference between other cars, pedestrians, cyclists, traffic lights, and road signs.
- Track Moving Objects: The system anticipates where that pedestrian stepping off the curb is headed or what that other car changing lanes is about to do.
- Understand Scene Context: It reads lane markings to stay centered and makes sense of complex situations like a four-way stop.
This nonstop analysis allows the car to make split-second calls—braking for an obstacle, yielding to an ambulance, or stopping for a red light. Every safe maneuver is proof of the software’s ability to interpret the visual world just like a person would, but without ever getting tired or distracted. These examples show how far photo recognition has come from just tagging photos, becoming a core technology that’s pushing society forward.
The Rise of AI Images and The Need for Verification
The very same intelligence that lets a machine identify a cat in a photo can now create a picture of a cat that never existed. This double-edged sword has created a massive challenge for digital trust. What started as a niche experiment with AI-generated content is now a mainstream flood, and it's brought a wave of new risks along with it.
We're suddenly dealing with sophisticated misinformation, brand attacks, and new types of fraud, all built on images that look perfectly real. Your average photo recognition tool is completely fooled by this. It was trained to see a dog and label it "dog," not to ask if a real camera was ever involved.
When Seeing Is No Longer Believing
This is where a new class of verification tools comes into the picture: AI image detectors. While standard photo recognition software is great at categorizing what’s in an image, it has a blind spot when it comes to an image's origin.
An AI detector is different. It’s a specialist. Instead of looking for objects, it’s trained to hunt for the tiny, almost invisible artifacts that generative AI models leave behind. Think of them as digital fingerprints—subtle inconsistencies in lighting, unnatural textures, or microscopic patterns that our eyes would never catch.
For example, a specialized tool like AI Image Detector is built to spot these tell-tale signs.

This analysis doesn't just give a "yes" or "no" answer. It provides a confidence score, giving you a solid basis for judging an image's source instead of just going with your gut.
Protecting Credibility in a Synthetic World
This kind of verification is becoming non-negotiable for anyone whose reputation relies on authentic sources. For journalists, researchers, and brand safety teams, a single fake image can unravel everything.
- For Journalists: Confirming a photo from an anonymous source is fundamental to ethical reporting. An AI detector is now a key tool for stopping visual misinformation before it spreads.
- For Researchers: Academic integrity is built on real data. These tools help ensure images used in studies haven't been fabricated.
- For Brand Safety Teams: A company’s reputation can be tanked by a convincing deepfake or malicious synthetic image. Verification is the first line of defense.
The ability to tell a real photo from an AI-generated one isn't a technical luxury anymore. It’s a basic requirement for trust in digital communication. Without it, the line between fact and fiction simply dissolves.
Facial recognition, a key part of the photo recognition world, is one of the fastest-growing areas in tech. As you can explore in this detailed facial recognition analysis from Technavio, this growth brings both opportunity and risk. Bad actors are all over AI-generated faces, using them for everything from identity theft to elaborate social engineering scams.
Ultimately, as AI image generators get better and easier to use, the demand for powerful verification tools will only climb. These systems add a crucial layer of scrutiny, helping us all navigate the murky waters of modern media with a little more certainty.
Choosing The Right Photo Recognition Tool
With so many photo recognition tools on the market, picking the right one can feel like a shot in the dark. Whether you're a developer needing an API for a new app, a business owner managing a huge product catalog, or a journalist trying to verify an image's origin, the "best" tool really comes down to what you need it to do.
It’s tempting to get drawn in by flashy features, but the real trick is to look past the marketing and focus on what truly matters for your project. The first step is always getting crystal clear on your goals. Are you trying to identify thousands of different objects in a cluttered scene, or do you need a super-secure system for facial verification? Answering that question alone will point you in the right direction.
Define Your Core Requirements
Before you even glance at a vendor’s website, take a moment to map out exactly what you need. This simple exercise will save you a ton of time down the road and keep you from paying for a system that’s either too weak or way more powerful than you need.
Start by asking yourself a few key questions:
- What’s the main problem I'm solving? Is this for content moderation, building a visual search engine, or automating data entry? A tool built for security surveillance is going to have a completely different skillset than one designed for social media tagging.
- What kind of volume are we talking about? Will you process ten images a day, or is it more like ten thousand a minute? The scale of your operation will determine if a simple off-the-shelf solution will work or if you need a high-throughput, scalable API.
- How accurate does it need to be? For a fun photo-sorting app, an 85% accuracy rate might be perfectly fine. But for something like medical image analysis or verifying financial documents, you’ll need a system that gets it right closer to 99% of the time.
Getting these fundamentals down will drastically narrow your search, letting you filter out the noise and focus only on the tools that genuinely fit your needs.
Comparing Photo Recognition Solutions
To make the decision a little easier, it helps to see how different types of solutions stack up against each other. Each approach has its own strengths, so the best fit depends entirely on your project's specific demands—from budget and technical skill to privacy concerns.
Here’s a quick comparison to guide your thinking:
| Solution Type | Best For | Key Advantages | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud-Based APIs | Developers & businesses needing scalable, pre-trained models for common tasks. | Easy integration, no infrastructure to manage, pay-as-you-go pricing. | Data is sent to a third-party server, potential privacy risks, less customization. |
| On-Premise Software | Organizations with strict data security, compliance, or privacy requirements. | Full control over data, high level of security, customizable to specific needs. | Higher upfront cost, requires in-house technical expertise to maintain. |
| Open-Source Libraries | Researchers & developers with deep technical skills building custom solutions. | Complete flexibility, no vendor lock-in, free to use and modify. | High complexity, steep learning curve, requires significant development time. |
| Privacy-First Tools | Fact-checkers, journalists, and users handling sensitive or personal images. | Processes images locally or without storing them, builds user trust. | May have a more focused feature set compared to large cloud platforms. |
Ultimately, the goal is to find the sweet spot between power, usability, and cost. A large e-commerce company might benefit from a robust cloud API, while a healthcare provider would almost certainly need a secure on-premise solution.
Evaluate Performance and Integration
Once you have your requirements lined up, it’s time to get into the technical details. Performance isn't just about a high accuracy score; it's also about speed, reliability, and, most importantly, how smoothly the software can plug into your existing systems.
This is where the API (Application Programming Interface) becomes a huge deal. A well-documented, flexible API is what allows your own software to "talk" to the recognition service, making automation possible. For instance, a good API lets a developer build a system that automatically tags user-uploaded photos on a website, which can save a massive amount of manual work.
When you’re kicking the tires on a potential tool, look closely at:
- Speed: How fast can it process an image? For anything happening in real-time, like live video analysis, even a tiny delay can be a dealbreaker.
- API Documentation: Is it actually helpful? Clear, comprehensive documentation with code examples can make integration a breeze. Vague or confusing docs can turn it into a nightmare.
- Supported Formats: Does it handle the file types you actually use? Make sure it works with common formats like JPEG, PNG, and modern ones like HEIC or WebP.
A powerful recognition model is only useful if it's accessible and responsive. Prioritize tools that offer not just high accuracy but also a smooth, well-supported integration experience that fits your technical environment.
Prioritize Privacy and Ethical Use
In the world of image analysis, privacy isn't a feature—it's a foundation for trust. This is non-negotiable for any software that handles personal photos or sensitive visual data. Many services ask you to upload your images to their cloud servers for processing, and you might not have any idea how long they're stored or what they're used for.
This common practice opens up some serious risks. Those stored images could be exposed in a data breach or used to train future AI models without your consent. This is why finding a privacy-first tool is so important. Look for a photo recognition software provider that processes images on the fly and explicitly states that they do not store your data.
This commitment to privacy helps you stay compliant with regulations like GDPR and, more importantly, keeps the trust of your users. If you want to dig deeper into this, our detailed guide to picture recognition software explores the privacy landscape in more detail.
Finally, think about the ethics behind the tool. An AI model is only as good—and as fair—as the data it was trained on. If a model was trained mostly on images from one demographic, it might be less accurate and introduce bias when analyzing images of others. Don't be afraid to ask vendors how they work to mitigate bias and ensure their training datasets are diverse and representative. Making a responsible choice protects not just your organization but also the people whose images are being analyzed.
Frequently Asked Questions About Photo Recognition
Even after getting a good handle on photo recognition, some specific questions always seem to pop up. Let's tackle the most common ones to clear up any lingering confusion you might have about this technology.
What’s The Difference Between Image Recognition And Object Detection?
Think of it like this: image recognition gives you the big picture, while object detection focuses on the details.
Image recognition looks at an entire photo and gives it one main label. It might see a picture and say, "This is a park in autumn." It gets the general theme or setting.
Object detection, on the other hand, is much more specific. It goes a step further by finding and pointing out individual items inside that same photo. In that same park scene, it would draw little boxes around a "person," a "bench," a "dog," and a "tree."
So, image recognition answers, "What's this a picture of?" Object detection answers, "What specific things are in this picture, and where are they?"
How Accurate Is Photo Recognition Software?
This is a great question, but the answer isn't a single number. The accuracy can swing wildly depending on the job it's doing and the quality of the image it’s given. For clean, controlled tasks like matching a high-quality passport photo for identity verification, the best systems can hit an accuracy of over 99%.
But in the real world, things are rarely that perfect. Performance can drop off quickly when conditions aren't ideal. The biggest culprits are:
- Image Quality: Blurry, poorly lit, or low-resolution photos are a nightmare for algorithms to read correctly.
- Task Complexity: It’s one thing to spot a car, but it’s a whole different challenge to identify a rare species of bird or a specific model of industrial machinery.
- Algorithmic Bias: This is a big one. If a model was trained on a dataset that wasn't very diverse, its accuracy will be much lower for groups or situations that were underrepresented in its training data.
So, while the technology is incredibly powerful, its real-world accuracy really depends on the specific application and the data you feed it.
Can Photo Recognition Software Detect AI-Generated Images?
This is a critical misconception. The short answer is no, not really.
Standard photo recognition software is trained to answer, "What is in this image?" It learns the patterns that make up a cat, a car, or a sunset. It has absolutely no training on how an image was created.
Since AI-generated images are designed from the ground up to perfectly mimic the patterns of real photos, they easily fool these systems. To spot fakes, you need a different kind of tool altogether: an AI image detector.
An AI image detector is trained for a totally different mission. Instead of learning to identify a dog, it learns to find the tiny, often invisible digital artifacts, unnatural patterns, and subtle inconsistencies that generative models leave behind. It’s looking for the very clues that standard recognition software is programmed to ignore.
What Are The Privacy Concerns With Photo Recognition?
The privacy concerns are huge, especially when it comes to facial recognition. The heart of the issue is how biometric data—your unique face print—is collected, used, and stored.
Here are the main worries:
- Unauthorized Data Collection: Companies have been caught scraping billions of images from social media and public websites to build massive facial recognition databases, all without anyone's consent.
- Surveillance and Tracking: There's a real fear of this tech being used for widespread public surveillance, which chips away at personal anonymity and has serious implications for civil liberties.
- Data Breaches: If a company's database of faces gets hacked, that biometric data is out there forever. Unlike a password, you can't just change your face.
This is why choosing privacy-first tools is non-negotiable. Look for services that process images without storing them and are completely transparent about their data policies. For any business dipping its toes into this technology, respecting user privacy isn't just good ethics—it's essential for building trust and staying on the right side of regulations like GDPR.
Ready to add a crucial layer of trust and verification to your workflow? AI Image Detector helps you instantly determine if an image is human-made or AI-generated. Our privacy-first approach means your images are never stored, ensuring complete confidentiality. Get clear, reliable results in seconds. Try it for free today.


