What Is a Real Image and How Do You Spot a Fake
The term "real image" has taken on a double life. It holds one meaning rooted in the physics of light and a second, more urgent meaning tied to digital truth. Put simply, a real image is a photograph captured by an actual camera in the real world—not a synthetic picture cooked up by artificial intelligence. That distinction is now the front line in the battle to verify what we see online.
What a Real Image Means Today

For decades, defining a "real image" was a straightforward concept straight out of a physics textbook. It described how a lens focuses light rays onto a single point to create an image you could project onto a surface. Think of a movie projector or the way a camera sensor captures focused light to make a photograph.
But the explosion of powerful AI image generators has completely redefined the conversation. Today, when we ask if an image is real, we’re almost always asking something else: Is it authentic? Was this picture snapped in the physical world, or was it fabricated by an algorithm? This modern definition is less about optics and more about origin and trust.
The Two Sides of Authenticity
To really get it, you have to think of a real image as having two identities that must match up: the physical and the digital.
- The Physical Origin: This is the classic part. Light from an actual scene travels through a lens and hits a sensor. This process is inherently imperfect, leaving behind telltale signs like lens flare, subtle distortions, and organic, chaotic shadows.
- The Digital Fingerprint: Every genuine photo carries a unique digital fingerprint. This includes hidden metadata (EXIF data) that records camera settings, timestamps, and sometimes even the location. It also contains invisible patterns like sensor noise—tiny flaws unique to that specific camera, almost like a signature.
AI-generated images have no genuine link to the physical world. They aren't captures of light; they are mathematical constructions built pixel by pixel from learned data. While they can mimic reality with shocking accuracy, they often lack the natural flaws and the underlying data that prove where they came from.
Real Image vs AI Image At a Glance
Here’s a quick comparison of the core characteristics that distinguish a genuine photograph from a synthetic AI creation.
| Characteristic | Real Image (Human-Captured) | AI-Generated Image (Synthetic) |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Light from a physical scene | Algorithm based on training data |
| Flaws | Natural imperfections (lens flare, noise) | Unnatural glitches (weird hands, odd textures) |
| Metadata | Rich EXIF data (camera, settings, time) | Often missing, generic, or fake |
| Consistency | Consistent physics (light, shadows, reflections) | Inconsistencies in physics and logic |
| Digital Noise | Unique sensor noise pattern | Lacks a natural noise signature |
This table highlights the fundamental differences. A real image is an artifact of a physical event, while an AI image is a calculation.
The challenge of sorting authentic captures from synthetic media has become a global problem. During a recent year of intense global elections, fact-checkers flagged over 2.5 million suspicious images, discovering that a staggering 40% were confirmed as AI-generated.
This flood of synthetic content has sparked a massive demand for verification tools. The market for AI detectors—which are essential for confirming human-captured photos—is expected to climb from USD 0.69 billion in 2025 to USD 4.81 billion by 2033. As detailed in this AI detector market report, this growth shows an urgent need for reliable ways to confirm what's real.
Understanding both meanings of a "real image"—the optical and the authentic—is the first step toward navigating our increasingly complex visual world with confidence.
How a Real Image Is Born From Light

To really get what a real image is, we need to follow the light. The simplest way to think about it is with a movie projector. A projector shoots light through a film, then uses a lens to focus all those light rays onto a screen. That image you see on the screen? It's a real image, because the light rays physically come together—they actually meet—right there on that surface to create a picture.
A camera does the exact same thing, just in reverse. Instead of projecting an image out, it pulls one in. Light from the scene in front of you—a person, a landscape, whatever—travels into the camera's lens. The lens then gathers those rays and focuses them onto a digital sensor (or film, in the old days). Where all that light converges is where the real image forms.
This physical process is the core difference between a genuine photograph and a synthetic creation. A real image is a direct record of photons that journeyed from a scene, passed through a lens, and landed on a sensor. It’s a physical event, frozen in time.
The Perfect Imperfections of Reality
When a camera captures light, the process is never truly perfect. The real world is messy, and the hardware we use to record it leaves its own unique fingerprints all over the image. These aren't defects; they're signatures of authenticity—proof that the image was born from a physical process.
Think of them as the image's birthmarks. They can be subtle, but they're powerful clues that tell a story to a trained eye or a forensic tool. AI-generated images, having no physical origin story, can only try to imitate these quirks, and they often get the details wrong.
Here are a few of the most common physical signatures:
- Lens Distortion: No lens is perfect. They all bend light in slightly unique ways, causing straight lines near the edges to curve (barrel distortion) or creating faint color fringes around sharp edges (chromatic aberration).
- Natural Bokeh: When you focus on a subject, the background blurs into what’s called bokeh. The quality of that blur—its smoothness, the shape of the highlights—is a direct result of the physical blades inside the lens aperture.
- Sensor Noise: Every digital sensor has a unique, faint pattern of noise, like a fingerprint. This Photo-Response Non-Uniformity (PRNU) is a consistent artifact stamped onto every single photo taken by that specific camera.
These physical markers are the bedrock of image verification. An AI can paint a photorealistic scene, but it struggles to replicate the beautifully chaotic interaction of light with one specific lens and one specific sensor. This is where AI often gives itself away, leaving behind a sterile perfection that just doesn't feel right.
The Digital Breadcrumbs Left Behind
Beyond the physical artifacts baked into the pixels, a real image also carries a digital trail. When a camera saves a photo, it embeds a ton of information right into the file itself. This hidden data is called EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format) data.
This metadata acts like a digital birth certificate, recording the exact conditions under which the photo was born. It tells a rich story that an AI-generated image simply doesn't have.
A genuine EXIF record will usually contain:
- Camera Make and Model: The specific camera that took the shot (e.g., Sony A7 IV, Canon EOS R5).
- Lens Information: The type of lens used and its focal length.
- Exposure Settings: The nitty-gritty details like shutter speed, aperture, and ISO.
- Timestamp: The exact date and time the photo was taken.
- GPS Coordinates: Many cameras can tag the precise location of the shot.
Sure, this data can be removed or faked, but its presence and consistency offer a strong layer of evidence. An image with missing EXIF data, or with data that contradicts what you see in the photo, is an immediate red flag. The journey from light to pixels leaves a trail, and learning to follow it is the first step to verifying any image you come across.
Why Verifying Real Images Is Now Essential
Figuring out what's real and what's fake online isn't just for tech gurus anymore. It's a skill we all need. The ability to trust what we see has huge implications for everything from our faith in the news to the fairness of our legal systems.
When that trust is broken, the fallout is swift and serious. A doctored photo can tank a reputation, warp public opinion with lies, or completely discredit an important news story. In a world where convincing fakes can be made in seconds, the burden of checking the facts falls on all of us.
The Stakes in Journalism and Media
For journalists and fact-checkers, this is the new front line in the fight against misinformation. The entire mission of journalism—to report the truth—is under threat when AI can create photorealistic images of events that never happened.
A single fake photo can delegitimize an entire news organization. Imagine a major outlet publishing a gripping image from a conflict zone, only to have to retract it hours later because it was AI-generated. The damage is already done. Public trust, once gone, is incredibly hard to win back. This is precisely why newsrooms are putting iron-clad verification rules in place for every single visual they publish.
Legal and Corporate Integrity
In a courtroom, the authenticity of a photo can make or break a case. Photographic evidence needs to be rock-solid, but deepfakes and AI edits introduce a whole new level of uncertainty. Lawyers and forensic experts now have to prove not just what an image depicts, but also that it’s not a synthetic creation or has been tampered with.
For businesses, the risks are just as real. Fake images are perfect for phishing scams, creating fraudulent IDs, or spreading lies about a brand. The first step in securing digital content is making sure the source is credible, which is why strong user authentication systems are so important on platforms handling sensitive info.
The explosion of synthetic media is hard to overstate. The global market for AI image generators hit USD 9.10 billion in a single year, with a staggering growth rate of 38.16% CAGR. This flood of AI content means journalists and fact-checkers are swimming against a powerful tide. It's not just them; over 70% of creative professionals worry about AI blurring the lines with real art, creating a nightmare for copyright and authenticity. You can dive deeper into these numbers in the full AI market analysis.
This massive growth shows why knowing a real image when you see one has gone from a technical detail to a critical life skill.
Protecting Creative and Intellectual Property
Artists, photographers, and designers are facing a very personal threat. AI models learn by "studying" billions of images, many scraped from the internet without permission—and many of them copyrighted. An artist can wake up one day to find an AI perfectly replicating their signature style, churning out new works that mimic their own without credit or compensation.
This opens up a can of worms about ownership and what it means to be original. If an AI can generate a flawless copy of a photographer's work, what happens to their career? For creators, being able to verify an image's origin is about protecting their intellectual property and making sure human creativity doesn't get devalued. Our guide on verifying images for authenticity explores this challenge in more detail.
From the news we read to the art we love, the line between real and artificial is blurrier than ever. Verification isn't an extra step anymore—it’s a necessary habit for navigating our visual world with confidence. It’s about more than spotting fakes; it’s about defending the truth.
Your Practical Guide to Verifying Any Image
So, you want to get to the bottom of whether an image is real or not. The good news is, you don’t need a high-tech forensics lab to start figuring things out. By combining a few straightforward techniques, you can create a reliable workflow to spot the fakes.
The process is all about layers of verification, starting with what your own eyes can tell you and moving on to what powerful tools can uncover. Let’s walk through a simple, three-step approach: a manual check, a reverse image search, and finally, using a dedicated AI Image Detector.
Start With a Manual Visual Check
Before you even think about using a tool, just stop and look. Trust your gut. Our brains are surprisingly good at noticing when something in an image just feels… off. Even as AI generators get scarily proficient, they still slip up, especially with the finer details.
Slow down and scan the image for these classic giveaways:
- Anatomical Oddities: Zero in on hands, teeth, and ears. AI models are notorious for messing up hands, often adding an extra finger or creating joints that bend the wrong way. Teeth can look a little too perfect, and ears sometimes come out looking warped or misplaced.
- Unnatural Textures: Skin can have an overly smooth, almost plastic-like finish. Hair might look like a blurry, tangled mess instead of individual strands. Look for weird, repeating patterns in clothing or backgrounds that scream "digital."
- Physics Goof-ups: Pay attention to light and shadows. Are the shadows falling in the right direction for the light source? Do reflections in glass or on shiny surfaces actually match what’s around them? AI often struggles to get these basic laws of physics right.
Think of this initial inspection as your first line of defense. If you spot a few of these red flags, it’s a clear signal that the image deserves a much closer look.
Trace the Image Origin With a Reverse Search
After your visual check, the next move is to find out where the image has been online. A reverse image search is a surprisingly simple but incredibly effective way to uncover a picture's digital history.
This step helps you answer one crucial question: is this a new, original photo, or is it an old picture being passed off as something new? Tools like Google Images and TinEye make this dead simple. You just upload the image, and they’ll show you where else it has appeared across the web.
If the photo shows up on multiple, credible news sites tied to a specific event and date, that’s a good sign of its authenticity. But if it only appears on meme pages or has been floating around for years in completely different contexts, you should be highly suspicious.
By combining your visual inspection with a reverse image search, you build a much stronger case for or against an image's authenticity. This two-step process can often debunk a fake without needing more advanced tools, but for convincing fakes, you need to go one level deeper.
Use an AI Image Detector for a Definitive Answer
When your eyes tell you something is off but a reverse image search comes up empty, it’s time to bring in a specialist. An AI Image Detector is designed to spot the tiny, invisible artifacts that AI generators leave behind—clues that are completely hidden from the human eye.
These tools give you a clear, data-driven analysis to either confirm your suspicions or put them to rest. The process is quick and gives you a confidence score in just a few seconds.
Here’s a quick rundown of how to use our AI Image Detector:
- Upload the Image: Just drag and drop your image file (it works with JPEG, PNG, and WebP) right into the tool.
- Analyze the Results: The detector gets to work instantly, giving you a verdict like "Likely Human" or "Likely AI-Generated," along with a percentage-based confidence score.
- Examine the Heatmap: Many detectors, including ours, provide a visual heatmap. This is a color overlay on your image that highlights the specific areas the algorithm found most suspicious, showing you exactly what triggered the AI flag.
This flowchart shows just how critical image verification has become across different professional fields.
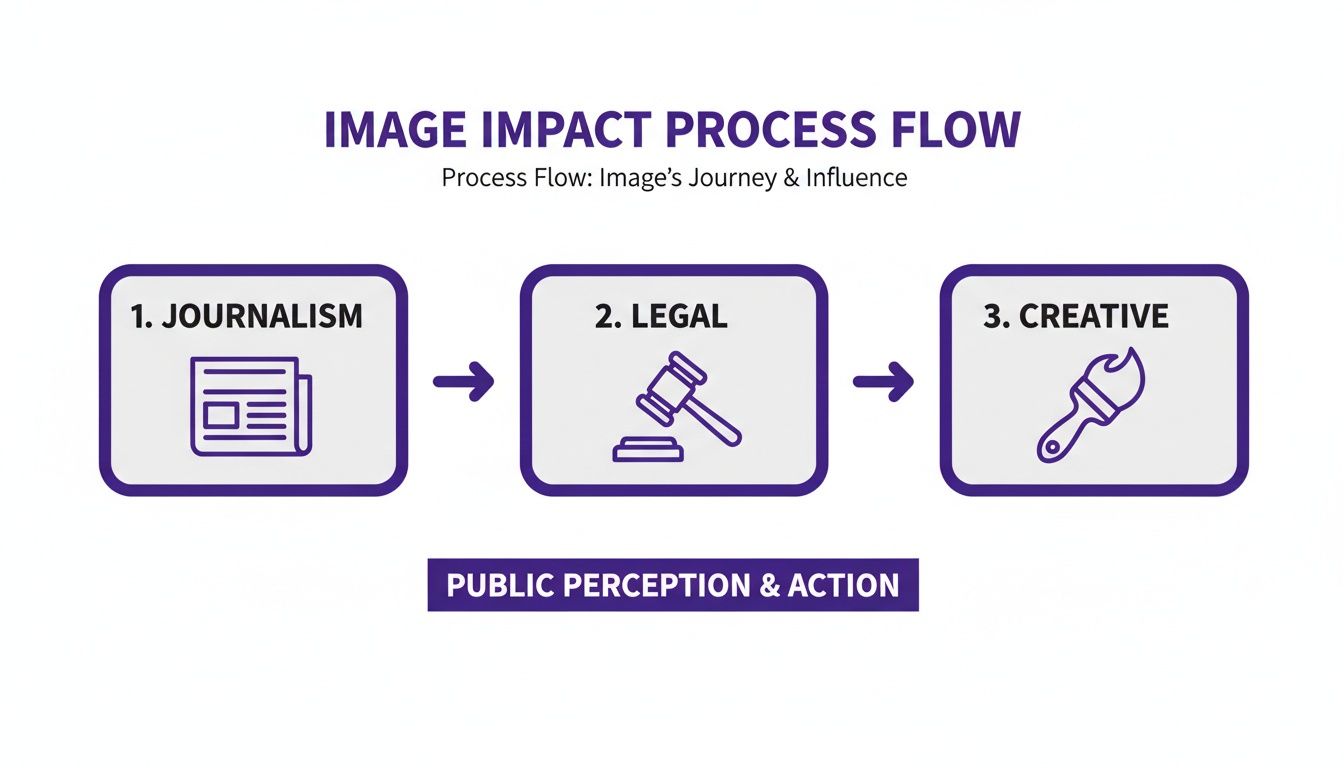
From journalism and law to creative industries, knowing an image is real is the first step in maintaining trust and integrity. You can dive deeper into these techniques in our full guide on how to check if a photo is real.
Using a dedicated tool like this adds that final, crucial layer of technical evidence, turning what started as a gut feeling into a solid conclusion.
Uncovering the Hidden Clues in Pixels
![]()
The human eye is pretty good at spotting obvious fakes—think of an AI-generated hand with six fingers or shadows that defy the laws of physics. But for the really convincing forgeries, a quick glance isn't enough. To truly figure out if an image is real, we have to go deeper, into the hidden world of pixels, where technical artifacts tell the true story.
Think of advanced detectors as digital forensic investigators. They're not just looking at the picture; they're searching for the subtle clues left behind when the image was created. For a genuine photo, that means finding the unique signature every camera sensor stamps on its work. For an AI-generated image, it means spotting the sterile, mathematical patterns that give away its synthetic origins.
The Camera Sensor Fingerprint
Every digital camera, from a professional DSLR to the one in your phone, has tiny, invisible imperfections in its sensor. This flaw, known as Photo-Response Non-Uniformity (PRNU), creates a faint but consistent noise pattern across every single photo that specific camera ever takes. It’s essentially the camera's permanent, unforgeable fingerprint.
Specialized detectors can pull this PRNU pattern out of an image. If a photo contains a consistent and authentic PRNU, it's powerful evidence that it came from a real camera.
A camera's PRNU is one of the most reliable indicators of authenticity. Because this fingerprint is a result of physical manufacturing quirks, AI models have an incredibly difficult time replicating it convincingly, making its presence a powerful sign of a real image.
Understanding how an image is processed is also part of the puzzle. For instance, using a secure image online resizer can sometimes alter or strip away these forensic markers, which is something investigators need to consider during verification.
Unmasking AI-Generated Patterns
Just as real cameras leave behind fingerprints, AI models leave their own digital footprints. An AI doesn't understand light or physics; it understands data and patterns. This leads to subtle but detectable artifacts that expose an image as a fake.
Below is a breakdown of the technical indicators that help separate the real from the synthetic.
Technical Indicators of Image Authenticity
| Indicator Type | Evidence in Real Images | Evidence in AI-Generated Images |
|---|---|---|
| Noise Patterns | Organic, random noise from the camera sensor (PRNU). | Repetitive, grid-like noise patterns; sometimes unnaturally clean. |
| Texture & Detail | Natural randomness and variation, even in repeating textures. | Textures can be too perfect, overly smooth, or have identical repeating elements. |
| Frequency Analysis | A natural distribution of high and low-frequency details. | An artificial signature with unusual spikes or gaps in the frequency spectrum. |
| Object Cohesion | Elements like hair, fur, or fabric blend logically and physically. | Strange blending, melting objects, or inconsistent details (e.g., mismatched earrings). |
These forensic clues are so important because they shift the conversation from subjective "does it look real?" checks to objective data analysis. It’s the same kind of thinking you’d use to detect photoshopped images, where you're looking for digital inconsistencies that betray manipulation.
The demand for this kind of scrutiny is absolutely exploding. The AI detector market is expected to skyrocket from USD 1.08 billion to USD 13.68 billion in just a decade. In the media world, one study of 1.8 billion social media posts found that 28% were flagged by detectors. Meanwhile, corporate risk teams now rely on these tools to catch 92% of deepfake fraud attempts during ID validation, showing just how critical they've become.
By getting a handle on these hidden clues, you start to appreciate the sophisticated cat-and-mouse game behind image verification. Every pixel tells a story—you just need the right tools to read it.
Common Questions About Image Authenticity
As we dig into what makes an image "real," a few questions always pop up. The technology is moving so fast that it's easy to get lost in the gray areas, the what-ifs, and what's coming next. Let's clear up some of the most common points of confusion.
What If a Real Photo Is Heavily Edited?
This is a fantastic question because it cuts right to the heart of a major gray area. Can a detector tell the difference between a heavily Photoshopped image and one generated from scratch by AI? The short answer is: usually, yes.
The key is understanding what the tools are looking for. When a human edits a photo—even heavily, by changing colors, removing objects, or blending images—they're still starting with a file that came from a camera. That means the original digital "fingerprint," like the unique noise pattern from the camera's sensor, is often still hiding in parts of the image.
An AI-generated image, on the other hand, is built from the pixel up. It has no camera DNA. Instead, it has its own synthetic tells, like unnaturally perfect gradients or subtle, repetitive digital textures.
- Human Edits: Often leave traces of the original photo, like inconsistent noise patterns between the edited and unedited areas.
- AI Generation: Creates an image with a consistent, but artificial, texture from corner to corner.
So, while a seriously manipulated photo can sometimes throw a detector for a loop, the more advanced tools can typically distinguish between human touch-ups and pure AI fabrication by analyzing these deep-seated patterns.
Are AI Image Detectors Ever Wrong?
Absolutely, and this is crucial to remember. No detection tool is 100% perfect. It's a powerful assistant, not an infallible judge. Like any analytical software, detectors can make mistakes, which typically fall into two buckets.
A false positive happens when a real, human-made photo gets incorrectly flagged as AI. This might occur with highly compressed JPEGs, some types of digital art, or photos that have been treated with aggressive noise-reduction software, which can accidentally scrub away the natural artifacts the detector looks for.
A false negative is the opposite: an AI-generated image slips past the goalie and is labeled as human. This is becoming more common as AI models get scarily good at mimicking the tiny imperfections that make photos look real.
This is precisely why an AI image detector should be one tool in your verification toolbox, not the only tool. Always back up its findings with a manual visual check and a quick reverse image search to build the strongest case for an image's authenticity.
Can AI Learn to Beat Detection Tools?
You've just hit on the central conflict in this entire field. It’s a constant cat-and-mouse game between the teams building AI image generators and the teams building the tools to spot them. As soon as detectors get good at identifying the tells of one generation of AI models, the next generation is trained specifically to cover those tracks.
Think about the classic example: early AI models were notoriously bad at drawing hands. Detectors quickly learned to flag images with mangled, six-fingered monstrosities. In response, AI developers fed their models better data and specifically trained them to generate perfect hands, making that old detection trick far less reliable.
This ongoing arms race means detection technology can never stand still. Researchers are constantly working on new methods that look for more fundamental clues—like subtle inconsistencies in the physics of light and shadow—that are much harder for an AI to fake. The goal is to stay one step ahead, but it’s a race that will probably never have a finish line.
Is Verifying Video Harder Than Verifying a Photo?
Yes, by a long shot. While the underlying principles are the same, verifying video is a whole different beast. A static photo is a single snapshot in time. A video is a sequence of thousands of those snapshots, all of which have to line up perfectly.
The challenge with deepfake videos isn't just creating one convincing frame; it's creating a seamless, believable flow of them.
Here's what makes it so much harder:
- Temporal Consistency: Every frame has to make sense with the one before and after it. Shadows have to move realistically, facial expressions must evolve naturally, and objects can't just flicker in and out of existence.
- Audio Syncing: In many deepfakes, the audio is also synthetic. The software has to check if the lip movements are in perfect sync with the generated voice, a task that demands incredible precision.
- Sheer Data: Analyzing a 30-second video clip means processing around 900 individual frames. This requires a massive amount of computational power compared to analyzing a single photo.
While deepfake detection technology is getting better every day, it's still playing catch-up to static image detection. The goal is the same—find the digital artifacts that give away the fake—but applying that across the dimension of time makes the problem exponentially more complex.
Don't leave authenticity to chance. Get a clear, fast, and reliable answer with the AI Image Detector. Upload an image now and see for yourself how easy it is to spot the difference between real and AI-generated content. Try it for free at aiimagedetector.com.



