Your Essential Guide to Using a Deep Fake Detector
A deep fake detector is essentially a digital forensics tool, built to analyze images and videos for subtle, machine-made errors that the human eye almost always misses. It uses advanced algorithms to spot the tell-tale signs of AI manipulation, acting as a powerful fact-checker to help you determine if a piece of media is authentic or synthetically generated.
Understanding How a Deep Fake Detector Works
Think of a deep fake detector as a highly specialized digital detective. Its main job is to scan a file—an image or a video—and hunt for the microscopic clues that give away its artificial origins. Even a well-made deepfake, one that could easily fool a person, often leaves behind a trail of subtle, nearly invisible errors that a machine can be trained to recognize.
This entire process is built on identifying what experts call 'digital artifacts.' These are the tiny inconsistencies and imperfections that AI models accidentally create when they generate or alter media. They're the digital fingerprints left at the scene.

Uncovering Digital Fingerprints and Artifacts
A robust deep fake detector doesn't just skim the surface; it dives deep into a file's code and pixel structure. These algorithms are trained on enormous datasets packed with millions of real and AI-generated images, which teaches them how to distinguish natural, organic patterns from synthetic, machine-made ones.
Here are some of the key artifacts these tools are trained to find:
- Unnatural Lighting and Shadows: AI often struggles with the physics of light. A detector can spot inconsistent shadows that don't align with the main light source in an image or video.
- Pixel-Level Inconsistencies: The tool scrutinizes the relationships between individual pixels, searching for odd patterns that simply don't occur in photos captured by a real camera sensor.
- Irregular Biological Signals: In videos, detectors look for unnatural blinking patterns (either too frequent or too sparse), stiff or jerky head movements, and poor lip-syncing where the mouth movements don't match the audio.
- Texture and Reflection Flaws: AI can stumble when rendering complex textures like hair, wood grain, or skin pores. It might also create bizarre or physically impossible reflections in a person's eyes or on shiny surfaces.
A deep fake detector's real power is its ability to see the unseen. It identifies the subtle, mathematical residue left behind by AI, turning a convincing fake into an easily identifiable piece of synthetic media.
The need for these tools is growing at an incredible pace. Valued at USD 114.3 million in 2024, the global deepfake detection market is projected to explode to USD 5,609.3 million by 2034. That's a compound annual growth rate of 47.6%, a figure that underscores the critical need for reliable verification in an age of widespread AI-generated content.
To give you a better sense of what these tools do, let's break down their core functions.
Core Functions of a Modern Deep Fake Detector
| Capability | What It Does | Why It Matters for Users |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-Model AI Analysis | Scans files using a suite of different AI detection models simultaneously. | Different AI generators leave different fingerprints. Using multiple models catches a wider variety of fakes and reduces false positives. |
| Deep Media Scanning | Analyzes the file's metadata, compression history, and pixel structure, not just the visible image. | This uncovers hidden clues about a file's origin and editing history that a surface-level scan would miss. |
| Privacy-First Processing | Processes files in real-time without ever storing them on a server after the analysis is complete. | Ensures confidentiality for sensitive content, like journalistic sources, legal evidence, or personal photos. |
| Confidence Scoring | Provides a clear percentage-based score indicating the likelihood that the media is AI-generated. | Offers a straightforward, easy-to-interpret result, helping users make quick and informed decisions without needing technical expertise. |
These capabilities work together to provide a comprehensive and trustworthy verdict on the authenticity of digital media.
A Privacy-First Approach to Verification
For anyone handling sensitive content—whether you're a journalist protecting a source, a legal team reviewing evidence, or a company verifying customer IDs—privacy is non-negotiable. That's why modern detection tools are built with a privacy-first architecture.
When you upload a file for analysis, the process happens in real-time. Critically, the image or video is never stored on the provider's servers. The system processes the data, delivers the verdict, and then immediately discards the file. This ensures your content remains completely confidential.
This secure, no-storage model is essential for professionals who need both accuracy and security in their workflows. You can learn more about how this works in our guide to the modern fake detector machine.
How Deepfake Detectors Spot a Fake
Think of a deepfake detector less like a futuristic sci-fi scanner and more like a seasoned art fraud investigator. A casual glance might fool you, but the expert isn't looking at the big picture. They’re zeroing in on the microscopic brushstrokes, the chemical composition of the paint, and the tell-tale signs of forgery that an artist—or in this case, an AI—leaves behind.
These tools are trained to hunt for specific digital fingerprints that fall into two main buckets: visual artifacts in still images and temporal inconsistencies in videos. Let's break down what that actually means.
Unmasking Flaws in a Single Frame
Getting an AI to generate a photorealistic image is one thing. Getting it to create one that holds up to intense scrutiny is another beast entirely. The AI has to get everything right—not just the person's face, but the way light bounces off their glasses, the texture of their shirt, and the logic of the world around them. This is where it often stumbles.
That’s when pixel-level analysis comes into play. It's like putting a digital photo under a high-powered microscope. The detector scans for unnatural patterns that just don't show up when a real camera captures an image. It might spot weird color blotches, skin that’s too smooth and lacks any pores, or the bizarre, blurry seams where a generated face meets real hair.
But the clues go beyond just the pixels. Detectors also look for context errors—things that just don't make sense. The AI might create a stunningly realistic person but stick them in a room where the text on a background sign is gibberish or they're wearing earrings that seem to defy gravity. These are huge red flags.
Lighting and shadows are another dead giveaway. Our brains are pretty good at glossing over minor lighting mistakes, but a machine is ruthless in its analysis.
- Conflicting Shadows: The detector checks the direction and softness of every shadow. If a person's shadow points left, but the shadow from the lamp next to them points right, it's a strong signal that elements were stitched together from different sources.
- Unnatural Reflections: Take a close look at someone's eyes or glasses in a photo. AI generators are notoriously bad at creating believable reflections. You’ll often find blurry, distorted, or completely nonsensical scenes mirrored back.
- Inconsistent Light Sources: If a person’s face is lit brightly from the right, but the room around them is clearly lit from the left, a detector can easily flag this as a digital manipulation.
Imagine an investigator gets a photo of a politician in a supposed scandal. It looks real. But a detector highlights that the shadow from the politician's nose is completely out of sync with the shadow from the desk lamp. That one subtle flaw can be all it takes to expose the entire image as synthetic.
The big idea with static image detection is that AI struggles with holistic consistency. It might nail one part, like a face, but it often fails to make that part live logically within the rest of the scene.
Spotting Inconsistencies in Motion
Videos add the tricky dimension of time, which gives a detector a whole new set of potential slip-ups to hunt for. These are called temporal inconsistencies—unnatural changes or movements that happen from one frame to the next. A fake photo only has to be perfect for a single moment. A deepfake video has to maintain that illusion flawlessly across thousands of frames. It's a much harder trick to pull off.
One of the most famous tells is unnatural blinking. Real people blink regularly and naturally. Early deepfakes often featured subjects who blinked way too often, almost never, or not at all. While the models have gotten better, strange blinking patterns are still a key signal detectors are trained to catch.
But it goes way beyond just blinking. Detectors are also on the lookout for other biological cues that AI has a hard time faking.
- Stiff or Jerky Head Movements: Sometimes a deepfake is just a digital mask layered over an existing video. If that mask doesn't move in perfect sync with the real person's head, you get stiff, robotic, or slightly laggy motions.
- Poor Lip-Syncing: A classic giveaway. If the audio doesn't quite match the movement of the speaker's lips, something is wrong. A detector can analyze the audio's phonemes (the sounds of speech) and cross-reference them with the visual mouth shapes on a frame-by-frame basis.
- Lack of Subtle Emotion: Real human expressions are complex, involving tiny muscle movements—micro-expressions—all over the face. AI-generated faces often look unnaturally smooth or "frozen," missing the subtle twitches that convey genuine emotion.
These clues over time give a detector a mountain of evidence to work with. By tracking these tiny errors as they pile up, the tool can build a powerful case for whether a video is real or fake, turning fleeting imperfections into a clear verdict.
Putting a Deep Fake Detector to Use
Knowing the theory is one thing, but the real test is putting a deep fake detector to work confidently in your day-to-day workflow. It's time to move from abstract concepts to practical, repeatable steps that can genuinely safeguard your work.
The core process is surprisingly simple, no matter your profession. You upload your media, look at what the detector tells you, and then use that information to make a smarter decision. The trick is to treat the tool's output not as a final, unassailable verdict, but as a crucial piece of evidence in a larger puzzle.
This mindset is absolutely critical in high-stakes fields like journalism or platform safety, where the authenticity of a single image can have massive ripple effects.
A General Workflow for Verification
No matter what you're trying to verify, a solid process follows the same fundamental pattern. You want to combine the lightning speed of an automated tool with the nuanced critical thinking that only a human can provide. Think of the deep fake detector as your first responder—it gives you a quick assessment that helps you know where to dig deeper.
Here’s a simple, four-step process you can adapt to just about any situation:
- Upload the Media: Get your image or video file into the detector. Most modern tools are built for speed and can give you an initial read in under ten seconds.
- Analyze the Confidence Score: The first thing you'll see is the AI-generated score. This might be a percentage or a clear label like "Likely AI-Generated," giving you an immediate sense of the odds.
- Review Highlighted Inconsistencies: The best tools don't just give you a score; they show their work. They’ll often highlight specific areas in the image that scream "AI artifact." Pay close attention to these zones—they’re your starting point for a manual review.
- Corroborate with External Methods: This is the most important step. Never rely on the tool alone. Use its findings as a lead to inform your next steps, whether that’s a reverse image search, checking the source’s credibility, or looking for other reports on the same piece of media.
This structured approach is how you use the technology responsibly. To give you a better idea of what's happening under the hood, this visual breaks down the core principles of analysis that a detector automates.
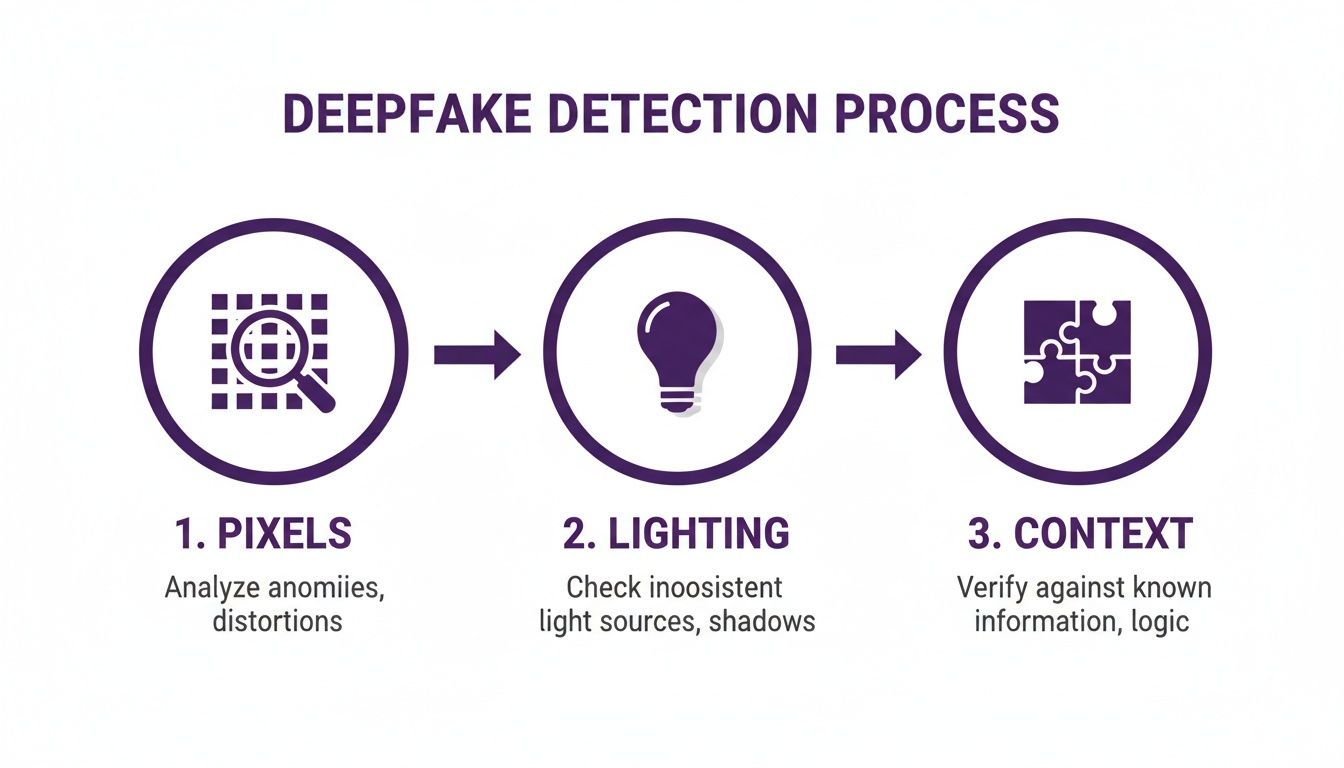
As you can see, the analysis moves from the tiny details (pixels) to the bigger picture (context). It’s the same process a seasoned human fact-checker would follow, just supercharged with technology.
Verification Checklists for Professionals
Different jobs come with different challenges when you’re dealing with synthetic media. A journalist vetting a tip from an anonymous source has very different needs than a trust and safety team sifting through thousands of new user profiles. Here’s how you can tailor your approach.
For Journalists and Fact-Checkers
When you're up against user-submitted content or a viral image spreading like wildfire, you need speed and accuracy. The game is to filter out the obvious fakes fast so you can focus your energy on the content that's genuinely suspicious.
- Initial Triage: The moment unverified visual media comes across your desk, run it through a deep fake detector. Make it a reflex.
- Source Scrutiny: If an image gets flagged as "Likely AI," it's time to put the source under a microscope. Who sent it? What’s their track record?
- Context is King: Does the image or video even make sense? Cross-reference what it depicts—the location, the weather, the people involved—with established facts.
- Seek Original Copies: Always push for the highest-resolution version of the file. Compression is the enemy of verification and can sometimes obscure the tell-tale signs of manipulation.
For Educators and Researchers
In an academic setting, the goal is two-fold: teaching digital literacy and protecting the integrity of your source material. A deep fake detector serves as both a verification tool and a powerful teaching aid.
- Classroom Demonstrations: Show, don't just tell. Use a detector in class to demonstrate how shockingly easy it is to create convincing fakes—and how they can be spotted. Our guide on how to check for AI usage offers more ideas for practical lessons.
- Verifying Academic Sources: When you’re evaluating visual evidence in a research paper or a historical archive, a detector can help spot anachronistic edits or synthetic "enhancements."
- Promoting Digital Skepticism: Make verification a habit. Encourage students to run any suspicious images they find online through a detector as a standard part of their research process.
The explosion of synthetic media has made digital verification a non-negotiable skill. Deepfake detection software is quickly becoming essential, with the market projected to hit USD 4.7 billion by 2033, growing at an annual rate of 20.9%. This isn't just a niche tool; it's a response to an urgent, global need for content authentication.
For Trust and Safety Teams
If you're working for a platform that handles user-generated content, your biggest challenge is sheer volume. You can't manually review everything. Automated detection is your only real defense against an onslaught of fake profiles, fraudulent posts, and harmful content.
- API Integration: The most effective approach is to integrate a detection API directly into your content upload workflow. This lets you screen every single image automatically.
- Flagging and Queuing: Use the detector's confidence scores to set up rules. You can automatically flag suspicious content for a human to review while letting clearly authentic media pass through without a hitch.
- Pattern Recognition: The data from the detector is a goldmine. Use it to spot patterns of malicious behavior, like one user creating dozens of accounts with different AI-generated profile pictures.
Of course, detection is only half the battle. Knowing how to respond when you do find a deepfake is just as important, which is why solid communications crisis management is key to keeping user trust. By adopting these kinds of role-specific workflows, you can go from simply owning a tool to building a truly robust system for digital authentication.
Interpreting Your Detection Results
Running a file through a deepfake detector is just the first step. The real work starts when you have to make sense of the results. You'll rarely get a simple "real" or "fake" answer. Instead, you'll see a spectrum of labels, like "Likely Human" or "Highly Likely AI-Generated." This isn't a flaw in the system; it's a critical feature.
Why the nuance? Because absolute certainty in AI detection is a myth. The technology is caught in a perpetual game of cat-and-mouse, with new AI generation techniques popping up all the time. A probabilistic score is the only honest way to reflect this reality, giving you a measure of confidence instead of an impossible guarantee.

Why Results Are Like a Weather Forecast
Think of a detection score like a weather forecast. When a meteorologist says there's a 90% chance of rain, you grab your umbrella. It’s not a cosmic guarantee that it will rain, but all the data points very strongly in that direction. A high AI-generated score is the same kind of thing—it’s a strong, evidence-based assessment, not a magic eight-ball.
On the flip side, a 10% chance of rain means you can probably leave the umbrella behind, but you know a freak shower isn't completely off the table. A low AI score suggests the media is probably authentic, but it’s not an ironclad seal of approval. This whole framework is designed to help you make informed decisions based on risk and probability.
Just as a forecast pulls together data from satellites, radar, and atmospheric models, a deepfake detector synthesizes clues from pixel artifacts, lighting inconsistencies, and digital fingerprints. The score is the combined weight of all that evidence.
This approach is essential for using these tools responsibly. It forces us to think critically and reminds us that a detector is a powerful assistant for human judgment, not a substitute for it.
Handling Mixed or Inconclusive Results
So, what happens when the results are murky? You'll sometimes get an inconclusive score because the file is a hybrid—part human, part AI. This is becoming incredibly common with photos that have been heavily manipulated with AI tools, like replacing a background or removing an object.
These "hybrid" images are everywhere. An authentic photo might have one person digitally erased and replaced, or its lighting completely changed with an AI filter. In these situations, the detector is actually working perfectly; it sees traces of both human and machine creation and gives you a score that reflects that ambiguity.
When you get an inconclusive result, don't throw your hands up. It’s a signal to put on your detective hat and dig deeper.
A Protocol for Inconclusive Scans
An ambiguous scan isn't a dead end—it's a signpost telling you it's time for some manual verification. Here’s a simple checklist to run through when the detector isn't giving you a clear yes or no:
- Cross-Reference with a Reverse Image Search: This is your first move. Use a tool like Google Images or TinEye to find other places the image has appeared online. This can often lead you straight to the original, unedited source, showing when it first surfaced and in what context.
- Scrutinize the Source's Credibility: Where did this file come from? Was it a reputable news organization with a track record of getting things right? Or did it pop up on an anonymous social media account known for spreading chaos? The source's credibility provides powerful context.
- Look for Corroborating Evidence: Can you find other, independent sources that back up what the image claims to show? If a photo supposedly captures a specific event, search for other photos, videos, or news reports from that same event. A total lack of corroboration is a massive red flag.
By combining the powerful analysis of a deepfake detector with these classic verification techniques, you build a much more resilient process for separating fact from fiction.
Choosing the Right Detection Tool for You
Picking the right deepfake detector isn't just about finding a tool that works. It’s about finding one that fits perfectly—and securely—into how you already operate. The reality is, not all detectors are created equal, and the best one for you will depend on a delicate balance of privacy, speed, and how it integrates with your existing workflow.
For most professionals, whether you're a journalist verifying a source or a researcher authenticating evidence, the tool has to be frictionless. Features like no-registration access are a must. You shouldn't have to jump through hoops, create an account, or hand over personal data just to check a single image. It should be quick and confidential, period.
Efficiency is just as critical. A solid deepfake detector needs to give you answers in under ten seconds, letting you quickly sift through suspicious content. It also absolutely has to support common file types like JPEG, PNG, and WebP, so you can analyze media from pretty much anywhere without wasting time on conversions.
Prioritizing Privacy in Your Selection
In an era of constant data breaches, a 'privacy-first' approach isn't just a nice-to-have; it's the gold standard. For anyone handling sensitive or confidential material, this is non-negotiable.
A truly privacy-first detector processes your file on the fly and—this is the crucial part—does not store the image on its servers once the scan is done. The tool does its job, gives you a result, and immediately forgets the file ever existed. This setup guarantees that your sensitive content, whether it's legal evidence, a confidential source, or a personal photo, stays completely private. Opting for a tool without this protection is an unnecessary risk.
Scaling Up with API Integration
While individual users value speed and privacy, businesses and developers are up against a different beast: sheer volume. Think about social media platforms, online marketplaces, or any service dealing with tons of user-generated content. Manually checking every single upload is simply not an option. This is where API integration becomes a lifesaver.
An Application Programming Interface (API) lets you plug deepfake detection capabilities directly into your own platforms. It’s what allows you to run automated, real-time screening at a massive scale.
By integrating a detection API, a platform can instantly scan every new profile picture for signs of AI generation, flag fraudulent marketplace listings using synthetic images, or identify coordinated misinformation campaigns as they unfold.
This automated first line of defense is absolutely essential for maintaining trust and integrity on your platform. It's no surprise that the deepfake AI market is dominated by this approach, with cloud-based API deployment making up 69.66% of the market in 2024. Services from major providers can run as low as USD 0.10 per minute, putting powerful detection technology within reach for even smaller teams. For a deeper dive into these market dynamics, the deepfake AI market report from Grand View Research is a great resource.
Feature Comparison for Deep Fake Detectors
When you're evaluating different services, it helps to have a checklist. The table below breaks down the essential features to look for, why they matter, and what an ideal implementation looks like.
| Feature | Why It's Important | Ideal Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| No-Storage Policy | Protects your sensitive data from being stored, leaked, or misused. | The service explicitly states that files are deleted immediately after analysis. |
| API Access | Allows for automated, high-volume detection integrated directly into your applications. | Well-documented, easy-to-use API with clear pricing and robust support. |
| Fast Processing | Enables rapid verification, crucial for workflows like news reporting or content moderation. | Results are returned in under 10 seconds per file. |
| Broad File Support | Ensures you can analyze images from various sources without format conversion headaches. | Supports major formats like JPEG, PNG, and WebP at a minimum. |
| No Registration | Provides frictionless, anonymous access for quick, one-off checks. | The tool can be used directly from a web interface without creating an account or providing an email. |
| Clear Reporting | Delivers easy-to-understand results, helping you make informed decisions quickly. | Provides a simple confidence score (e.g., 99% Human) and highlights areas of manipulation. |
Ultimately, finding the right tool is about matching its capabilities to your specific security needs and operational scale.
For more guidance on the nuances of detection, check out our in-depth article on advanced deep fake detection strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions About Deepfake Detectors
With deepfake tools becoming more common and easier to use, people are naturally asking more questions about how to spot them. If you're serious about digital verification, you need to understand what deepfake detectors can and can't do. Let's walk through some of the most common questions to give you a clearer picture.
We'll cover how accurate these tools really are, whether they can be tricked, and the legal side of using them. The goal is to give you the context you need to use a detector effectively.
How Accurate Is a Deepfake Detector?
Even the best deepfake detector on the market isn't 100% infallible, and it's important to understand why. Think of a detector less like a magic eight ball and more like a highly trained specialist. Top-tier tools are constantly being updated, with their AI models retrained to spot the tricks used by the very latest deepfake generators.
This is exactly why you'll see results presented as confidence scores—something like "95% Likely AI-Generated"—instead of a simple "real" or "fake." It's an honest acknowledgment that this is a moving target.
A deepfake detector is a powerful instrument, but it's one part of a larger verification process. It gives you a crucial, data-driven starting point, but it should always be combined with other methods like checking the source or doing a reverse image search.
This approach gives you a more nuanced and realistic assessment, helping you make an informed judgment instead of relying on a black-and-white answer that might not capture the full story.
Can a Deepfake Detector Be Fooled?
Yes, absolutely. The world of deepfake creation and detection is a constant cat-and-mouse game. As soon as detectors get good at spotting a certain artifact—say, weird-looking ears—the next generation of deepfake models learns to create perfect ears. This technological arms race means no single detector can be permanently foolproof.
However, where AI still struggles is in flawlessly mimicking the thousands of tiny, subtle patterns that make us human. Modern detectors are trained to hunt for these microscopic inconsistencies, which are incredibly difficult for an AI to get right all the time, across every frame.
Even the most advanced deepfakes often slip up on things like:
- Natural Blinking: AI frequently gets the rate and duration of human blinks wrong. It sounds small, but it's a huge tell for a trained detector.
- Blood Flow Simulation: High-end detection tools can actually analyze pixel-level color changes to spot the faint, rhythmic pulse of blood under the skin on a real person's face. That’s something a completely synthetic image just doesn't have.
- Physical Consistency: AI can struggle with the basic physics of light. Unnatural shadows, bizarre reflections in the eyes, or textures that just don't look right are all red flags a sophisticated detector is built to catch.
So while a very well-made fake might get past one specific check, it's much harder to fool a system that runs a multi-layered analysis looking for dozens of these tell-tale signs at once.
Is It Legal to Check an Image with a Detector?
In almost all cases, yes, using a deepfake detector to analyze a file for authenticity is perfectly legal. It’s a standard practice in fields like journalism, academic research, and online content moderation where confirming the integrity of digital media is part of the job. The act of analysis is simply about figuring out where a file came from and if it's been manipulated.
The important thing to remember is the distinction between analyzing the image and what you do with it afterward. The legality of using the detector is totally separate from the copyright and privacy laws that apply to the image itself.
Here’s the simple breakdown:
- Analysis: Checking an image to see if it’s AI-generated is generally fine.
- Usage: If you publish, share, or use that image without the proper rights, you could be breaking copyright or privacy laws—and that’s true whether the image is real or fake.
Think of a detector as an investigative tool. Using it for its intended purpose of verification is a standard and legal practice for professionals who need to trust the media they work with.
Ready to separate authentic images from AI-generated fakes with confidence? The AI Image Detector offers a free, fast, and privacy-first solution. Get a clear confidence score in seconds without ever needing to register or worry about your images being stored.



